$3.8 Million Funds Houston Methodist's Chikungunya Vaccine Research

Scientists at the Houston Methodist Research Institute recently received $3.8 million to develop further a promising type of disease-defense technology that could pave the way for new 'circular RNA' vaccines.
The Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) announced on January 25, 2024, that it is teaming up with the Houston Methodist vaccinology team to advance its 'circRNA' vaccine development platform.
As the name suggests, circular RNA vaccine technology uses a closed-loop RNA, which could enable vaccine candidates based on it to be more stable and durable than current linear-based mRNA candidates.
This high-impact innovation offers significant potential beyond mRNA vaccines in defending populations against future epidemic and pandemic disease threats.
While mRNA vaccines are now expected to play a crucial role in preventing and controlling future outbreaks and pandemics, they have some limitations – including the potential to provoke local reactions or short-term fever in people who receive them, says CEPI.
"We are excited to be working with CEPI on developing circular RNA vaccine technology to protect the world against emerging viral threats," said H. Dirk Sostman, M.D. President and CEO of the Houston Methodist Academic Institute, in a press release.
"This effort is led by Dr. John Cooke, director of our Center for RNA Therapeutics, with a team of innovative scientists including Drs. Dan Kiss, Jimmy Gollihar, Kristopher Brannan, and Francesca Taraballi, together with our colleagues at the University of Texas Medical Branch."
"Houston Methodist is leading medicine by generating fundamental scientific insights that have transformational effects on human health."
Initially targeting the Chikungunya virus, a member of the Togaviridae family, the Houston Methodist project aims to generate the data necessary to establish preclinical proof of concept for the vaccine candidate.
As of late 2023, the U.S. FDA has approved Valneva SE's IXCHIQ® Chikungunya Vaccine, a monovalent, single-dose, live-attenuated chikungunya vaccine.
Chikungunya is a viral disease transmitted to humans by infected mosquitoes, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Yellow Book 2024.
Chikungunya outbreaks were initially recorded in Thailand in 1967 and India in the 1970s.
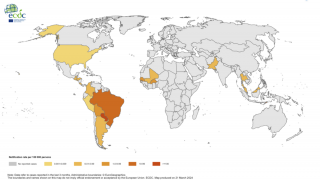
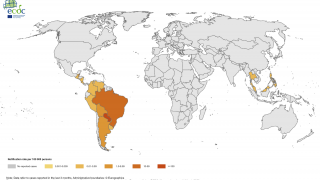
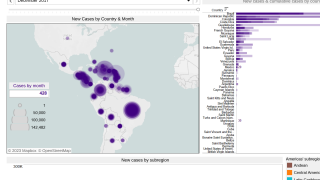
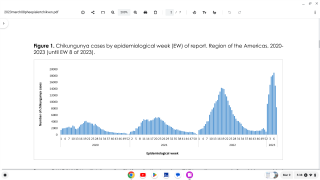
In 2023, the World Health Organization said chikungunya outbreaks were identified in over 100 countries, primarily in the Region of the Americas,
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee