Brazil Spends Millions Modifying Dengue-Carrying Mosquitoes

The Federative Republic of Brazil recently deployed two science-based methods to reduce the impact of its multi-decade dengue virus outbreak.
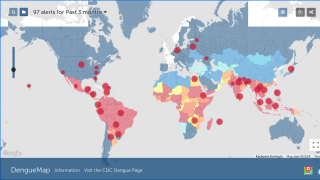
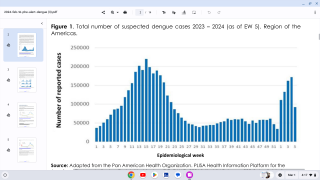
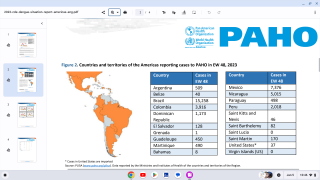
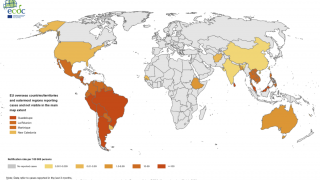
Dengue re-emerged in Brazil in 1981 and has perpetually increased the number of cases, reaching about 2,909,404 cases and a case fatality rate of 0.049% for 2023.
As Brazil's Ministry of Health offers Takeda's second-generation QDENGA® vaccine, it also deploys a one-time intervention to protect Brazilians from dengue and other mosquito-borne diseases such as Zika.
To support Brazil's states and municipalities. The health department transferred R$256 million (about $500m) to reinforce the fight against dengue.
Brazil uses the Wolbachia method as an additional strategy for controlling dengue outbreaks.
The initiative involves releasing Aedes aegypti mosquitoes infected by an intracellular bacterium of the genus Wolbachia. This process blocks the transmission capacity of dengue viruses by mosquitoes.
According to the World Mosquito Program, Wolbachia is a safe, natural bacteria that has evolved to live inside the cells of up to 50% of insects.
Wolbachia cannot survive outside of insect cells because it does not have the necessary machinery to replicate itself without help from the insect host. This means Wolbachia cannot survive in the real world.
When Wolbachia mosquitoes are released, they breed with wild mosquitoes. Wolbachia-modified mosquitoes eventually replace the local mosquito population.
Once Wolbachia is established in the population, it stays there for many years.
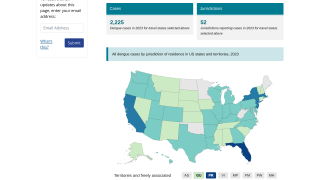
In the United States, the Wolbachia method has been deployed in Florida since 2017. In the U.S., the use of mosquitoes with Wolbachia is regulated by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
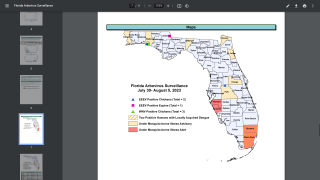
During 2023, the Florida Department of Health issued mosquito-borne illness advisories for dengue and malaria.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee