Ebola Cases Restart in the DRC

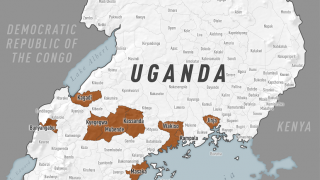
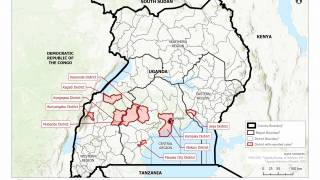
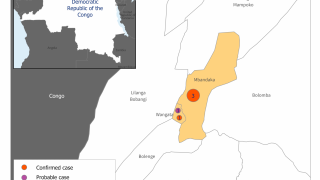
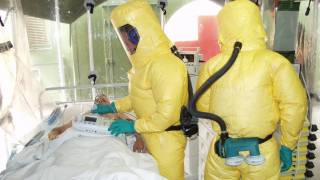
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has recently reported 3 new Ebola Zaire infections, according to the World Health Organization.
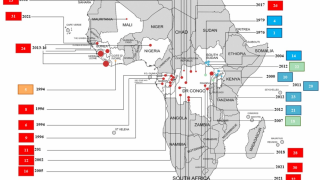
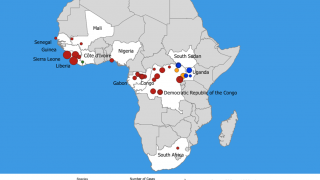
As of April 12, 2020, a total of 3,457 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) cases were reported, of which 2,277 cases died (overall case fatality ratio 66%).
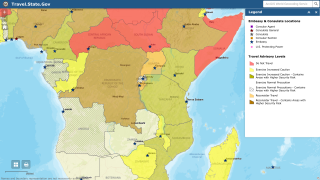
Given this new data, the International Health Regulations Emergency Committee for Ebola in the DRC met on April 14, 2020, and has reaffirmed its view that this Ebola outbreak continues to constitute a Public Health Emergency of International Concern.
The WHO Director-General endorsed the Committee’s advice and issued them as Temporary Recommendations under IHR (2005) to reduce the international spread of EVD.
The Director-General thanked the Committee Members and Advisors for their advice and requested their reassessment as soon as the situation requires.
‘We have to anticipate and be prepared for additional small outbreaks. We need the full force of all partners to bring these outbreaks under control and to meet the needs of the people affected,’ said the WHO in a statement.
Previously, the WHO announced it was requesting additional funding on February 20, 2020. Under the Strategic Response Plan, the WHO’s financial need for the Ebola Response from January to June 2020 was determined to be $83 million dollars.
Additionally, the Committee provided the following advice regarding the DRC:
- Intensify surveillance activities and investigation of recently reported cases including potential nosocomial infections.
- Expand the use of vaccines in high risk populations, as vaccination is the best public health tool to prevent and control the spread of EVD.
- Continue to strengthen the EVD infrastructure (i.e. primary health care, risk communications and community engagement systems such as community action cells, surveillance systems including at points of entry, and alert management levels).
- Reinforce messaging with communities regarding the potential for resurgence and the need for sustained community engagement in reporting of alerts.
- Remain vigilant against EVD while strengthening the focus on routine immunization programs as well as other vaccine-preventable diseases (i.e. measles and polio).
The Ebola virus, also known as Zaire ebolavirus, Sudan ebolavirus, and Bundibugyo ebolavirus, can cause severe hemorrhagic fever, leading to high case fatality rates (30–90%) in humans.
Ebola prevention vaccines are given to help protect people from getting Ebola disease.
- Ervebo, known as V920 in its investigational phase (rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP), is a recombinant, replication-competent Ebola vaccine.
- Ad26.ZEBOV/MVA-BN-Filo is a heterologous prime-boost Ebola vaccine regimen.
In the USA, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says ‘there have been 49 travelers who were ill when returning to the USA from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) or the surrounding African countries since August 2018.
Of these 49 individuals, testing for Ebola was recommended for just 1 person.
The good news from the CDC is that person tested negative for Ebola and was subsequently treated for malaria.
In the USA, presumptive testing for the Zaire ebolavirus is now available at 69 Laboratory Response Network laboratories located in 49 states, which are accessible through coordination with state or local public health authorities.
Ebola medication and vaccine news published by Vax-Before-Travel.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee