RSV Monoclonal Antibody
RSV Monoclonal Antibody 2024
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is a leading cause of respiratory disease in children and older adults. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) says RSV monoclonal antibody monoclonal (mAb) therapy prevents serious lower respiratory tract disease (LRTD) caused by RSV in newborns and young children during their first RSV season. The World Health Organization (WHO) published its preferred product characteristics of mAb therapy that delivers passive immunization against RSV disease.
The JAMA Network published an Original Investigation on February 17, 2023: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 14 randomized clinical trials assessing the efficacy and safety of nirsevimab, motavizumab, and palivizumab that were associated with significant reductions in RSV-related hospitalization, infection, and supplemental oxygen use on children.
RSV Monoclonal Antibody Therapy
AstraZeneca and Sanofi co-developed Beyfortus™ (Nirsevimab-alip), a single-dose, long-acting mAb designed to protect infants through their first and second RSV seasons. The European Commission granted Beyfortus worldwide approval on November 4, 2022, followed by approval from the U.K., Canada, and the USA.
Synagis® (Palivizumab) is a multi-dose injectable RSV antibody that provides one month of protection, requiring five injections to cover a typical RSV season. The U.S. FDA (1998), Canada, Japan, Israel, the U.K., and India (2023) have approved Synagis to protect at-risk infants against RSV.
Motavizumab is a discontinued investigational RSV mAb. MedImmune filed the original BLA in January 2008.
RSV Monoclonal Antibody Candidates
Shanghai Ark Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd. announced on November 23, 2023, that it had received IND approval in China from the National Medical Products Administration for a novel antibody, AK0610, targeting RSV. It is anticipated to protect infants throughout the entire RSV season. ArkBio licensed the drug's intellectual properties from the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Beijing Children's Hospital, Capital Medical University, and National Center for Children's Health.
RSV Deaths in Children
In 2022, the JAMA Network conducted an Original Investigation that found 96 (95% CI, 92-99) RSV deaths among children younger than one year. A study published by the Journal of Infectious Diseases determined that RSV-related deaths in infants <1 year peaked at about one month.
RSV Vaccines
RSV vaccine news is updated in 2024.
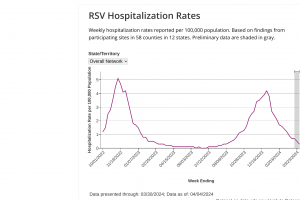
RSV Seasonality 2023
Data related to RSV seasonality for 2023 is posted at this link.