RSV Season
RSV Season 2024
As of March 4, 2024, the World Health Organization (WHO) Influenza Update N° 466 reported respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) activity was stable or decreased in the USA, Canada, Egypt, and most countries in Europe. RSV detections increased slightly in New South Wales of Australia, Mozambique, New Zealand, and South Africa.
RSV Season United States
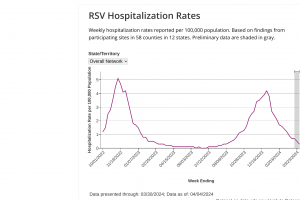
As of late February 2024, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported the national per capita RSV hospitalization rate was decreasing and remains lower than the November 2023 peak. The CDC's RSV detection graphs display the 5-week moving average in the U.S., indicating decreased cases in certain states. The National Emergency Department Visit RSV and Wastewater Scan data shows RSV detections in 2024. The CDC presented an Overview and Epidemiology of RSV Hospitalizations in Adults on October 25, 2023. The RSV-NET Interactive Dashboard shows for the 2022-2023 RSV season in the U.S., the overall rate of related hospitalizations was 50.9 per 100,000 people. The U.S. CDC Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report presented the seasonality of RSV in the U.S. from 2017–to 2023.
During the prepandemic and pandemic years, RSV circulation in the U.S. began in Florida, then migrated to the southeast, and later to the north and west regions. Florida's RSV season is longer than the rest of the U.S. and has distinct regional patterns, says the U.S. CDC. The Florida Department of Health reported as of February 3, 2024, RSV activity in Florida continued decreasing throughout the state as of week #5.
RSV Season the Americas
The Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) published a situation report in December 2023 confirming RSV activity has remained low overall. Still, several countries from the southern hemisphere (Brazil, Chile, Paraguay, Uraguay) reported a start of the 2023 RSV season. On May 23, 2023, an updated Protocol and Technical note regarding RSV laboratory diagnosis. SARInet updates the seasonality of RSV in Latin America and the Caribbean.
RSV Season Australia
As of October 2023, Australia's Department of Health and Aged Care published report #1; influenza-like-illness activity in the community has remained stable and was low overall. The number (1,652) and proportion of RSV notifications by age group and reporting period since January 2023 are linked here.
RSV Season Canada
RSV season in Canada typically runs from October until May, with most cases occurring in winter. As of September 17, 2023, updated RSV detection information in Canada for week 37 is posted at this link, including positive RSV tests in Canada segmented by region.
RSV Season Europe
The European Respiratory Virus Surveillance Summary (ERVISS) interactive dashboard provides a weekly RSV epidemiological summary for the European Union/European Economic Area (EU/EEA). By week #46 (ending 19 November 2023), the community's acute respiratory infection (ARI) rates were increasing in many EU/EEA countries. Rates of severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) cases presenting to secondary care were comparable to the same time last year.
RSV Season United Kingdom
The U.K. Health Security Agency reported in November 2023 that during week #46, the overall positivity for RSV increased slightly to 12.5%, with the highest positivity in those under five years at 38.7%. Hospital admission rates for RSV among those under five years decreased. The Joint Committee on Vaccination and Immunisation posted historical data on September 11, 2023. Following the June 2023 meeting, JCVI issued a short statement of its advice on an RSV immunization program. JCVI advised that an RSV immunization program that is cost-effective should be developed for both infants and older adults.
RSV Mortality
The JAMA Network published results from an Original Investigation in 2022 that reported a mean of 6,549 (95% CI, 6140-6958) underlying respiratory fatalities were associated with RSV each year. Most RSV deaths were among children <5 (47.8%) than adults ≥50 (40.4%) years of age.
RSV Adult Mortality
The U.S. FDA VRBPAC reviewed RSV Epidemiology and Disease Burden in Older Adults on February 28, 2023, presented by Fiona Havers, MD, MHS, FIDSA. On February 23, 2023, the U.S. CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) conducted a meeting on RSV. In adults aged 50 years, hospitalization rates for RSV were similar to those associated with influenza as of 2018. From 2005 to 2016, researchers identified 405 deaths in adults over 50. RSV-pneumonia deaths among adults aged ≥50 years were 17.6 in 2005.
RSV Infant Mortality
The U.S. CDC reports most infants are hospitalized with RSV during their first few months of life. The Lancet reported on February 14, 2024, a meta-analysis found that preterm infants face a disproportionately high burden of RSV-associated disease, accounting for 25% of RSV hospitalizations. They estimated that, in 2019, 533,000 hospital admissions of preterm infants in the first year of life occurred worldwide. Regarding mortality, these researchers estimated that, globally, 26,760 overall preterm infant deaths were attributable to RSV in 2019
A study published by PLOS Medicine on July 17, 2023, concluded that the RSV disease burden was high in the nearly 600 million children under five living in 121 low-income and middle-income countries. A study published by the Journal of Infectious Diseases determined that RSV-related deaths in infants <1 year peaked at one month, while bronchiolitis and influenza mortality peaked at two months. Over the 20-year study period, RSV was listed as the underlying cause of death on 932 death certificates. Children <1 year of age accounted for 39% of RSV and bronchiolitis deaths.
Over eight assessed RSV seasons, among children with a first infection, annual inpatient and outpatient reinfection rates were 0.25% (95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.22–0.28) and 3.44% (95% CI = 3.33–3.56), respectively. Both infection and reinfection rates declined with age.
The U.S. CDC RSV Work Group presented on June 23, 2022 - RSV Virion and Vaccine Products by Natalie Thornburg; Epidemiology of RSV in Children by Dr. M McMorrow. And the ACIP reviewed in February 2023 Maternal/Pediatric presentations led by Sarah S. Long, MD Chair, Maternal/Pediatric RSV Work Group: Nirsevimab for preventing RSV in infants; Jefferson Jones, MD MPH FAAP, Next Steps for the ACIP Maternal & Pediatric RSV Work Group.
The JAMA Network conducted an Original Investigation on February 28, 2022, that found there were 96 (95% CI, 92-99) RSV deaths among children younger than one year. A study published by the Journal of Infectious Diseases published a study in August 2022 determined that RSV-related deaths in infants younger than one year peaked at about one month.
Breastfeeding infants during the first few months of life protects against severe RSV bronchiolitis outcomes. Breastfeeding reduced the risk of hospitalization (OR 0.47, 95% CI 0.25 to 0.89, p=0.021). This review (Feb. 2022) shows that exclusive and partial breastfeeding reduces the severity of disease, length of hospital stay, and supplemental oxygen requirement.
RSV Pregnant Women
The Journal of Infectious Diseases published a meta-analysis of eleven studies in October 2023 that found that among 8,126 pregnant women, the proportion with respiratory infections that tested positive for RSV ranged from 0.9% to 10.7%, with a meta-estimate of 3.4% (95% CI: 1.9; 54). RSV hospitalization rates reported in two studies were 2.4 and 3.0 per 1000 person-years. Of five studies that ascertained RSV-associated deaths among 4708 pregnant women, no casualties were reported.
RSV Immunity
H. Keipp Talbot MD MPH FIDSA presented an RSV Immunity, Durability, and Reinfection overview during the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 179th Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee (VRBPAC) meeting on February 28, 2023. This conclusion said natural RSV infection does not provide durable or complete protection from reinfection; Anti-RSV antibodies return to pre-infection levels within six months after infection; RSV reinfection can occur within two months of the last infection; Older adults have weaker IFNγ responses to RSV than younger adults do, likely making older adults more susceptible to infection and to severe infection.
RSV, Influenza, COVID-19 Coinfections
On July 25, 2023, tests revealed that coinfections with two or more respiratory viruses occurred in 1.33% of positive results and .55% of the studied samples. The positivity rates varied by the viruses involved, ranging from .38% in adults for the SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) coronavirus and RSV to 2.28% in adults for influenza A and SARS-CoV-2. And a 6% coinfection rate of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza A in non-adults.
RSV Influenza Comparison
The JAMA Network published an Original Investigation on February 28, 2022: Mortality Associated With Influenza and RSV in the U.S., 1999-2018. This study suggests that RSV poses a greater risk than influenza to infants, while both are associated with substantial mortality among elderly individuals. Influenza has sizeable interannual variability, affecting different age groups depending on the circulating virus. A mean of 6549 (95% CI, 6140-6958) underlying respiratory deaths was associated with RSV annually, including 96 (95% CI, 92-99) deaths among children younger than one year. For influenza, there were 10 171 (95% CI, 9652-10 691) underlying respiratory deaths per year, with 23 deaths (95% CI, 19-27) among children younger than one year.
A study published in 2017 found that adult patients were less likely to be diagnosed with RSV than with influenza (2.3 vs. 8.3%, respectively), were older, and were more likely to be diagnosed with pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hypoxemia, and bacterial coinfection. Furthermore, in patients with RSV infection, the 20-day all-cause mortality was higher than that for influenza (18.4 vs. 6.7%, respectively). In addition, RSV infection showed a significantly higher risk of death than the seasonal influenza group, with a hazard ratio of 2.32 (95% CI, 1.17–4.58).
RSV Monoclonal Antibody Therapy
The RSV monoclonal antibody Beyfortus / Nirsevimab was FDA-approved in the U.S., and supply is increasing in 2024.
RSV Vaccines
As of 2024, two RSV vaccines have been approved in various countries.