Marburg Disease Outbreaks
Marburg Virus Outbreaks 2024
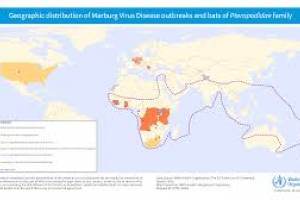
Marburg virus disease (MVD) was first recognized in 1967 In Germany and Serbia. As of 2024, Angola, DR Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Cameroon, Germany, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Serbia, South Africa, Tanzania, and Uganda have previously confirmed MVD cases. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) published Health Alert Network CDCHAN-00489 in 2023, confirming no cases of MVD have been reported in the United States, and has issued Travel Health Advisories focused on various MVD outbreaks.
Marburg Virus Disease Origin
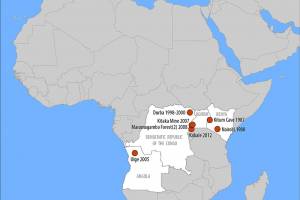
Marburg virus is a Filovirus that, along with the Ebola virus, can cause a severe and often fatal (fatality rate of up to 88%) viral hemorrhagic fever (VHF). MVD was observed for the first time in 1967 during an outbreak in Marburg a der Lahn and Frankfurt am Main, West Germany. Twenty-nine people developed clinical signs, and seven eventually died. Before developing the disease, all primary MVD cases directly interacted with grivets imported from Uganda or with grivet-derived tissues. Also, in 1967, workers involved in poliomyelitis vaccine development and production fell ill at different locations in Europe (Yugoslavia) associated with grivets imported from Uganda.
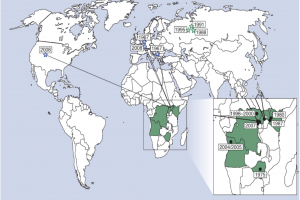
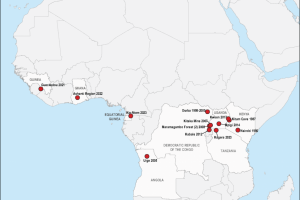
The History of Marburg Outbreaks' chronological list of known cases and outbreaks is published by the CDC. A systematic review published by The Lancet in November 2023 and the accompanying database provide a comprehensive overview of Marburg virus disease epidemiology and identify critical knowledge gaps. Research presented detailed information on 478 reported cases and 385 deaths from Marburg virus disease-estimate, an unadjusted, pooled total random effect case fatality ratio of 61.9% (95% CI 38·8–80·6; I2=93%).
A study published results on Jun. 8, 2023, suggests that GP does not entirely mediate the inability of MARV to cause lethal infection in ferrets but may, instead, be related to a block in multiple aspects of the replication cycle. As of 2023, virological.org says epidemiology and phylogenetic history argue for a zoonotic transmission event from a reservoir, presumably a bat.
Marburg Disease Prevention and Control Guidelines 2024
On Feb. 27, 2024, the WHO updated its Marburg infection prevention and control guidelines. The key recommendations are summarized in The BMJ.
Burundi Marburg Risk
The Republic of Burundi authorities confirmed via Twitter on March 28, 2023, the death of a third person following a mysterious illness that broke out in the northwest area. Local authorities have been ordered to prevent passengers from neighboring Tanzania from spreading Marburg disease.
Cameroon Marburg Risk
The Cameroon Regional Health Ministry reported two suspected MVD cases in the Olamze Commune on February 14, 2023. Cameroon previously restricted movement along the Equatorial Guinea border, restricted the movement of populations at the Cameroon - Equatorial Guinea border, and activated the incident management system throughout the region.
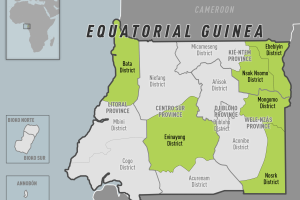
Equatorial Guinea Marburg Outbreak
The Republic of Equatorial Guinea (EG) confirmed its first-ever outbreak of MVD on February 13, 2023. The index case died in early January 2023. This outbreak was declared over on June 8, 2023. Since the outbreak declaration, 17 laboratory-confirmed cases of MVD and 12 deaths have been recorded (CFR 75%). The city of Bata in Litoral province is the most affected district, with nine laboratory-confirmed MVD cases reported. The U.S. Embassy in EG implemented a temporary policy under which official travel to the mainland region (Bata) by Embassy employees is only permitted for mission-critical needs, such as support for the MVD response.
Separately, the U.S. CDC updated its Level 2 travel alert regarding EG's MVD outbreak on May 12, 2023, stating, 'Reconsider non-essential travel to mainland Equatorial Guinea.' The U.K. says health professionals should remain alert for travelers returning from MVD-affected areas who develop symptoms compatible with MVD. Guidance and information about high-consequence infectious disease and their management in England and further information and guidance about Marburg fever are available from the UK Health Security Agency.
Europe Marburg Risk
The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) reported on March 25, 2023, that the likelihood of exposure and infection for EU/EEA citizens traveling or residing in the affected areas in Equatorial Guinea is currently very low. The most likely route of introduction of MVD into Europe would be via infected travelers. Should a case be imported, the likelihood of the spread of MVD within Europe is considered to be very low, says the ECDC.
Gabon Marburg Risk
The WHO Director-General stated on February 15, 2023, that the Gabonese Republic is preparing to rapidly detect, isolate, and care for suspected MVD cases. More than 163 people have crossed the borders between Equatorial Guinea, Cameroon, and Gabon.
Nigeria Marburg Risk
The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention confirmed in late February 2023 that there is a moderate risk of importing the Marburg virus into the country.
Spain Marburg Detection
VOA News reported on February 24, 2023, that a 34-year-old man who had recently traveled to Equatorial Guinea was diagnosed with Marburg disease. Reuters reported this man did not have Marburg disease on February 25, 2023.
Tanzania Marburg Outbreak
The United Republic of Tanzania's Ministry of Health declared the end of its first documented outbreak of MVD on June 2, 2023. Between 21 March and 31 May, nine cases were reported from Bukoba district, Kagera region. A total of six deaths (case fatality ratio 67%) were reported during the MVD outbreak. Additionally, the WHO advises against other international travel and/or trade measures in the United Republic of Tanzania. On March 27, 2023, the U.S. CDC issued a Watch - Level 1 Practice Usual Precautions, stating Tanzania had confirmed an MVD outbreak.
To ensure health systems fully recover from the effect of the outbreak and stay alert against future outbreaks, WHO has developed the 90-day Post MVD Recovery Operational Plan and is also supporting the Ministry of Health to develop the National 90-day Post MVD Recovery Plan. Survivor monitoring and support are ongoing in line with the National MVD Survivor Programme Guide developed during the outbreak.
Uganda Marburg Risk
Screening of travelers commenced at Kikagate Point of Entry in Isingiro District on March 27, 2023.
Marburg Virus Testing
Testing for Marburg virus and other causes of viral hemorrhagic fevers is available at CDC (Atlanta, Georgia) and within the Laboratory Response Network (LRN). As of April 2023, 32 geographically diverse LRN laboratories and 8 Regional Emerging Special Pathogen Treatment Centers can test using the Biofire FilmArray NGDS Warrior Panel. In addition, several more LRN laboratories are working toward building testing capability.
Marburg Disease Vaccine Candidates
As of 2024, the African CDC, the U.S. FDA, and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have not approved any Marburg vaccine candidate.
Marburg Outbreak News 2023
August 3, 2023 - NYC Health + Hospitals led a training exercise yesterday testing the health care system's ability to identify and isolate "patients" with simulated Marburg virus symptoms and safely transport them to NYC Health.