Tuberculosis Outbreaks
Tuberculosis Outbreaks 2024
On March 28, 2024, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported 9,615 TB cases provisionally reported by 50 states and the District of Columbia, representing an increase of 1,295 cases (16%) compared with 2022. On January 23, 2024, USAID published its Annual Tuberculosis Report to Congress, FY 2023, which indicated that 2022 global TB case notifications increased by 70% over the previous year. Globally, most people who developed TB were in the WHO Regions of Southeast Asia, Africa, Europe, and the Western Pacific. An estimated 1.3 million people died from TB in 192 countries and areas, led by India.
Tuberculosis Outbreaks United States 2024
Since 2020, TB case counts, and rates have increased yearly in the United States, according to the CDC. In January 2024, the CDC Tuberculosis Yellow Book 2024 reported immigrants from countries with a high TB burden and long-term residents of high-burden countries have a 10× greater incidence of TB than the US national average. I National case counts increased among all age groups, both U.S.-born and non-U.S.–born persons. On January 5, 2024, a second outbreak of bone allograft–related TB in recent years underscored the urgent need to implement improved donor screening and culture-based testing to prevent tissue-derived Mycobacterium tuberculosis transmission.
Alabama Tuberculosis - The Alabama Department of Public Health confirmed 92 TB cases in 2023, compared to 65 in 2022. As of July 31, 2023, seven confirmed or suspected TB disease cases have been identified in individuals who have worked in one or more poultry plants in Colbert, Franklin, Lawrence, or Lauderdale counties.
Alaska Tuberculosis - In 2023, Alaska reported the highest rate (10.6) of TB infections in the U.S. The CDC reported 96 TB cases in 2022, an increase of 70% (58) from 2021. Alaska reported the highest TB incidence (13.1). "We have this silent endemic disease that continues to linger, and it's going to take a lot of time and effort," Dr. Anne Zink, the state's chief medical officer, stated.
California Tuberculosis - Approximately 20% of all TB cases in the U.S. are reported from California. Similar to 2022 data (1,842), California reported an increase in TB cases in 2023 (2,113). In 2022, the California Health Department reported 1,750 TB cases in 2021, a 3% year-over-year increase.
Florida Tuberculosis - In 2023, Florida reported 624 TB cases. In 2022, Florida confirmed 536 TB cases. In 2021, 500 tuberculosis cases were reported in Florida, representing a 21% increase from 2020 (412). Miami-Dade County leads Florida in TB cases.
Illinois Tuberculosis - In April 2024, the Chicago Department of Public Health (CDPH) spokesperson Jacob Martin said they were "aware of a small number of TB cases among new arrivals in different shelters throughout the city." As of April 2024, CDPH does not provide routine TB screening services to the public. Illinois (including Chicago) reported 353 tuberculosis cases in 2023 and 298 in 2023.
Massachusetts Tuberculosis - The CDC confirmed Massachusetts increased TB cases from 154 in 2022 to 224 in 2023.
Michigan Tuberculosis—In 2023, there were 140 TB cases, an increase from 120 people with TB in 2022. The journal Clinical Infectious Diseases reported in January 2024 that spillover of enzootic M. bovis from deer to humans and cattle continues to occur in Michigan. Four people in Michigan recently contracted TB linked to wild deer and domestic cattle, increasing the total number of zoonotic cases in Michigan to seven since 2002.
New York - New York City Tuberculosis has confirmed over 500 cases of active tuberculosis as of 2023, an increase of roughly 20% from the same time in 2022. TB was diagnosed in every New York City neighborhood, with Flushing, Queens, having the highest rate, 22.4 per 100,000—more than three times higher than the city's overall rate. Data for New York indicates 894 TB cases in 2023 and 714 TB cases in 2022, an increase from 683 in 2021. NY Health Commissioner Ashwin Vasan explained in April 2023, "Many people who recently arrived in NYC have lived in or traveled through countries with high rates of TB."
Texas Tuberculosis - In 2023, Texas reported 1,235 TB cases, compared to 1,100 cases in 2022. Recent data indicates TB rates are accelerating in certain cities (Dallas, Ft. Worth, Hidalgo County, Houston, San Antonio) in 2024. About 69% of people diagnosed with TB in Texas were non-U.S. born. In 2022, 7,415 Texans were exposed to TB. Public health departments treated over 2,900 people for TB infection in 2022, and 50 Texans died of TB, the second most in any state. Harris Country (Houston) reported the most TB cases (267) in 2022. In 2021, 998 TB patients were reported throughout Texas, representing an increase of 12.5% from 2020. In 2019, Texas' 32 border counties had an average TB incidence nearly triple the national rate.
Tuberculosis Outbreaks United States 2023
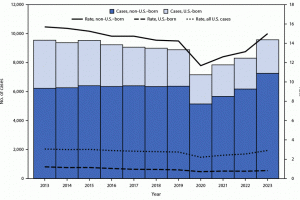
The U.S. CDC says TB case count increases in 2023 underscores the ongoing global TB-associated morbidity and mortality. In 2023, there was an increase of 1,295 cases (16%) compared with the 2022 total. The rate in 2023 (2.9 per 100,000 persons) also increased compared to 2022 (2.5). Forty states and DC reported increases th case counts and rates in 2023. Four states reported the most TB cases: California (22.2%), Texas (13.2%), New York (New York City) (8.6%), and Florida (6.4%). In 2023, 7,259 (76%) TB cases occurred among non-U.S.–born persons, an 18% increase compared with the 6,177 such cases reported in 2022. The number of cases in U.S.-born persons in 2023 with TB increased by 9%, from 2,131 in 2022 to 2,314. On October 5, 2023, H.R. 1776 was filed to require the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID), which leads the U.S. Government's global TB Strategy 2023–2030 efforts, to coordinate with federal agencies to update and implement programs for the global prevention, treatment, and eradication of tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis Outbreaks United States 2022
In 2022, among the 31,938 TB cases in US-born patients, researchers found substantially higher incidence among racial/ethnic minority populations. Compared with non-Hispanic Whites, TB incidence rate ratios were 4.4 times higher for Hispanics, 6.6 times higher for Asians, 6.8 times higher for Blacks, and 14.2 times higher for American Indian/Alaska Natives. In 2022, about 73% of reported TB cases that occurred in the U.S. were among non–U.S.-born persons.
Tuberculosis in The Region of The Americas
In the Americas, the PAHO reported about 325,000 people fell ill from TB in 2023, and 35,000 died from the disease, according to the World Health Organization's (WHO) Global Tuberculosis Report. In addition, an estimated 83,000 people went undiagnosed and untreated for TB.
Data indicates 31,000 TB cases (1,900 children) in Mexico in 2022. The U.S.-Mexico Binational Committees for Tuberculosis.
In 2022, 1,971 people in Canada were diagnosed with active TB disease, which was the underlying or contributing cause of death for 5.7% of those with TB, and people born outside of Canada represented 74.5% of active TB cases. In 2021, 1,904 active TB cases were reported in Canada. The corresponding incidence was 5.0 active TB cases per 100,000 population—estimates of TB burden in 2021.
Tuberculosis Europe
The World Health Organization (WHO) published the 2023 Global TB Report on November 7, 2023, which recommends TB preventive treatment for people with HIV, those with bacteriologically confirmed pulmonary TB household contacts, and clinical risk groups. Some people are infected with TB but are not sick, have a latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI), and can become ill in the future. Subclinical pulmonary TB, which presents without recognizable symptoms, is frequently detected in community screening.
The TB surveillance and monitoring report from the WHO Regional Office for Europe and the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) estimated that 229,000 people were diagnosed with TB in the European Region in 2022. In 2022, 53 WHO/Europe Member States reported 220,000 TB cases. The ECDC stated the EU/EEA is not on track to reach the goal of ending the TB epidemic by 2030.
Tuberculosis WHO South-East Asia Region
The Government of India's Central TB Division, within the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, will lead BCG vaccination efforts. India accounted for about 25% of the global TB burden. In 2021, the estimated TB incidence was 2,950,000, and an estimated 506,000 people died from TB. In 2020, compared to 2019, there was a 15.4% decrease in TB death totals, with 28 out of India's 36 states showing a decline. In addition, deaths by TB for individuals living with HIV decreased by 16% across India. The WHO's Global TB Report 2022 indicates that India's TB incidence was 210 per 100,000 in 2021. As of 2022, this WHO Region accounts for more than 45% of the annual global TB incidence (4.8 million) and more than half of global TB deaths.
Tuberculosis United Kingdom
The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) annual TB report shows tuberculosis cases in England rose 10.7% in 2023 compared to 2022 (4,850 compared to 4,380). In 2022, non-UK-born individuals born in India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Eritrea, Nigeria, and Romania continued to account for 79.1% of TB notifications in England. Tuberculosis cases in England in 2022 were stable compared to 2021 (4,380 in 2022 compared to 4,411 in 2021). In 2021, the highest TB rates were in London, accounting for 35.5%. The London TB Register shows that the rate of TB diagnosis is increasing. England was not on target to reduce TB incidence by 90% from 2015 to 2035. The BCG vaccine is no longer offered to children in secondary schools in the UK. It was replaced in 2005 with a targeted program for babies, children, and young adults at higher risk of TB.
Pre-Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Cases
A study published in April 2024 identified a high proportion (51%) of pre-extensively drug-resistant (pre-XDR) cases, followed by multidrug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) (15.5%). This correlates with the primary reason for a referral, as non-response to the first-line treatment (67%) and treatment failure or rifampicin resistance (14%). A multivariate analysis indicated that all young age groups, male gender, and Beijing strain were significant independent predictors of MDR-TB or MDR-TB+ [pre-extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) and XDR-TB].
Tuberculosis Case Ethnicity
The Lancet Infectious Diseases published a study on March 12, 2024, that found about 79% of people in Asia and Africa who had culture-confirmed pulmonary TB did not present with a cough, one of the symptoms most commonly associated with tuberculosis. In an April 2024 analysis of TB incidence rates for racial/ethnic populations, incidence rate ratios were 14.2 higher among younger American Indian or Alaska Native females.
Tuberculosis Outbreaks in Children
Each year, an estimated 1.2 million incident cases of tuberculosis occur in children younger than 15 years. Almost two-thirds of TB cases in children worldwide were either not reported or went undiagnosed and untreated. On March 28, 2024, the U.S. CDC's MMWR confirmed TB incidence increased in 2023 compared with 2022 among children aged 5–14 (68 cases, corresponding to a 42% increase in case count). The CDC reported 202 cases of TB in children ages four and younger in 2022, an increase from 160 cases in 2021.
Nontuberculous Mycobacteria
The CDC published a Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report on January 25, 2024, confirming nontuberculous mycobacteria skin infections across nine states linked to cosmetic surgery procedures and gaps in infection control at a clinic in Florida.
Zoonotic Tuberculosis Outbreaks
Tuberculosis (TB) is an ancient disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) that spreads through the air and affects people's lungs. "Consumption" and "Phthisis" were terms historically used to describe TB, which was responsible for one in four deaths in the 19th century. Zoonotic tuberculosis is a form of TB in people caused by Mycobacterium bovis, which belongs to the M. tuberculosis complex. There are an estimated 140,000 cases of zoonotic tuberculosis each year, which results in approximately 11,400 deaths. In 2022, Heads of State adopted the UN High-Level Political Declaration on the Fight Against Tuberculosis, reaffirming their commitment to ending the global tuberculosis epidemic, including a call for action against zoonotic tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis Tests
The U.S. CDC expanded its tuberculosis testing recommendations for people entering the U.S. on January 16, 2024. The instructions in this document supersede all previous Tuberculosis Technical Instructions, Updates to the Technical Instructions, and communications to panel physicians and international refugee resettlement organizations. These instructions must be followed for all applicants' tuberculosis disease screening and treatment. The molecular testing requirement, interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA) testing for adults, and changes to drug susceptibility testing (DST) defined in these instructions go into effect no later than October 1, 2024; all other components of these instructions go into effect January 24, 2024.
As of November 3, 2023, the U.S. CDC recommends testing persons at increased risk for TB infection as part of routine health care using TB blood tests, when possible, and prescribing a short-course treatment regimen if a diagnosis of LTBI is made. Among 3,647 healthcare providers, approximately 53% reported routinely testing non–U.S.-born patients for TB in 2023. On October 30, 2023, The Lancet published an assessment of the diagnostic accuracy of the Cepheid Mycobacterium tuberculosis Host Response prototype cartridge (MTB-HR) in children with presumptive tuberculosis. This candidate test measures a three-gene transcriptomic signature from fingerstick blood. MTB-HR differentiated children with culture-confirmed tuberculosis from those with unlikely tuberculosis with a sensitivity of 59·8% (95% CI 50·8–68·4). TB testing is expected to reach $2.7 billion in 2027 at a CAGR of more than 6%.
The journal Science Advances published results from a study on January 3, 2023, that data suggest that passive cough features distinguish TB from non-TB subjects and are associated with bacterial burden and disease severity. Although cough counts did not discriminate between coughs related to TB versus other conditions, cough scalogram characteristics were associated with identifying coughs due to pulmonary TB.
Tuberculosis Vaccines
There are various TB vaccines authorized worldwide as of April 2024.