Lyme Disease Outbreaks
Lyme Disease Outbreaks 2024
Lyme disease (Lyme borreliosis) is a bacterial disease transmitted to humans through the bite of infected ticks. Lyme disease is common in Europe, the United Kingdom, and the United States, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). In 1977, the first 51 cases of Lyme arthritis were described, and the Ixodes scapularis (black-legged) tick was linked to the disease transmission in Lyme, Connecticut. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported on February 15, 2024, that Lyme disease cases, the most common vectorborne disease in the United States, increased by 69%, 1.7 times the annual average during 2017–2019 in the United States.
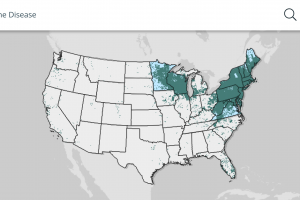
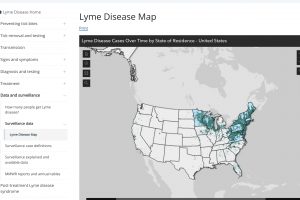
As of February 13, 2024, the U.S. CDC published a Lyme disease case map for the U.S. An estimate based on insurance records suggests that approximately 476,000 Americans are diagnosed and treated yearly for Lyme disease. From 2018 to 2022, a longitudinal study found the 51-to-60 age group made up 23.5% of Lyme disease private insurance claims in the U.S., according to an October 2023 infographic from FAIR Health. In 2022, Wisconsin, Vermont, Rhode Island, New Jersey, New Hampshire, Maine, Pennsylvania, and Connecticut were the leading states.
Lyme Disease Causes
Lyme disease is a tickborne zoonosis caused by certain species of Borrelia spirochetes. Ticks transmit at least 20 different disease-causing bacteria, viruses, and parasites to people, such as Lyme disease. The risk of contracting a tickborne infection and Lyme disease is determined by the number of ticks in an area, the proportion of those carrying the bacteria, and human behavior, such as walking in tick-infested fields. A study found the overall risk of developing Lyme borreliosis after a tick bite was 2.6% (95%CI 1.4–5.1).
Lyme Disease Outbreaks United Kingdom
In the U.K., the Health Security Agency says Lyme disease-carrying ticks are most active in the spring and summer. Approximately 4% of ticks are infected with Lyme disease in England and Wales, although this range can fluctuate in different areas and across years and can be, on average, as high as 8-10% in some areas. Around 1,500 laboratory-confirmed cases of Lyme disease are confirmed in England and Wales each. However, an estimated 1,000 to 2,000 more people are diagnosed yearly based on clinical assessment rather than laboratory tests.
Lyme Disease Outbreaks Europe
A review published in April 2023 showed substantial variability in reported Lyme Borreliosis incidence across and within European countries, with the highest incidences reported from the Eastern, Northern (Baltic states and Nordic countries), and Western Europe surveillance systems. The World Health Organization Europe says the number of Lyme disease cases in Europe has increased steadily, with more than 360,000 cases reported over the last two decades. Central Europe has the highest Lyme disease incidence, as reported by the Czech Republic, Estonia, Lithuania, and Slovenia. According to data released from Poland on April 24, 2023, 2,753 Lyme disease cases (a 93% increase) and 47 cases (a 236% increase) of tickborne encephalitis have been reported.
Lyme Disease Testing
IGeneX introduced, on April 18, 2023, culture-enhanced PCR testing (cePCR™) for all of the significant tickborne illnesses.
PrecisionVaccinations publishes Lyme disease vaccine news.