Malaria Vaccines
Malaria Vaccines 2024
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have recommended Mosquirix™ (RTS,S/AS01) and R21 / Matrix-M™ vaccines. These malaria vaccines were added to the WHO list of prequalified vaccines. The WHO's 2023 World Malaria Report, released on November 30, 2023, says the availability of two malaria vaccines is expected to increase supply and make broad-scale deployment across Africa possible.
The WHO says the annual global demand for malaria vaccines is estimated to be 40–60 million doses by 2026, increasing to 80–100 million doses annually by 2030. On April 25, 2026, the WHO Africa reported eight African countries now offer malaria vaccines and more than 30 countries in the African region are scheduled to roll it out in the next year through support from Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance. As of April 24, 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had not approved a malaria vaccine.
Malaria Vaccines Approved
Mosquirix™ RTS, S/AS01 (RTS,S) Malaria Vaccine - GSK's Mosquirix is a recombinant vaccine of the P. falciparum circumsporozoite protein from the pre-erythrocytic stage.
R21/Matrix-M™ Serum Institute of India's malaria vaccine was designed in 2011 and co-produced by scientists at the University of Oxford, Novavax AB, and Novavax Inc.
Malaria Vaccine Candidates
The Lancet Infectious Disease published in July 2023 results from a phase 1 study evaluating the effectiveness of the Gamete vaccine Pfs230D1-EPA/Alhydrogel to zygote vaccine Pfs25-EPA/Alhydrogel. Pfs230D1, but not the Pfs25 vaccine, induces durable serum functional activity in Malian adults.
RH5.1/AS01 Malaria Vaccine - RH5.1/AS01 is a novel recombinant malaria antigen developed at the University of Oxford.
The ProC6C-AlOH/Matrix-M vaccine candidate elicited the highest levels of functional antibodies in a phase 1 study, meriting further investigation.
BNT165 mRNA Malaria Vaccine - BioNTech is building the first vaccine for malaria based on mRNA technology to eradicate mosquito-borne illness. The phase 1 clinical trial evaluates the safety, tolerability, and exploratory immunogenicity of the 3-dose vaccine candidate BNT165b1 and is expected to enroll 60 U.S. volunteers with no malaria history.
BioNTech's Malaria project was first announced in July 2021.
Maryland-based Sanaria Inc.'s non-replicating whole parasite PfSPZ vaccine candidate is made with a live-attenuated form of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum sporozoite. Clinical studies have been shown to provide about 90% protection in a challenging clinical trial.
Ocean Biomedical has been awarded a new patent for a parasite target called PfCDPK-5. This target could potentially prevent the parasite at multiple stages in the malaria cycle in a multivalent mRNA-based malaria vaccine. In addition, recent studies in Nature identified PfGARP as a target of human antibodies that kill up to 100% of parasites in vitro.
AgTRIO mRNA-lipid nanoparticle was assessed for its potential usefulness as a vaccine against malaria.
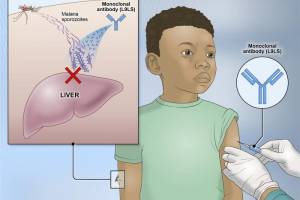
Malaria Monoclonal Antibody
The New England Journal of Medicine published results from a phase 2 study on April 26, 2024. The study demonstrated that a single subcutaneous injection of the NIAID's experimental L9LS (VRC-MALMAB0114-00-AB) malaria monoclonal antibody offered up to 77% protection against P. falciparum infection and clinical malaria over a period of six months.
The Phase 2 NIAID-USTTB clinical trial evaluated the safety and efficacy of a one-time, intravenous infusion of a monoclonal antibody called VRC-MALMAB0100-00-AB (CIS43LS). The antibody was found up to 88.2% effective at preventing infection over a 24-week period, demonstrating for the first time that a monoclonal antibody can prevent malaria infection in an endemic region. This antibody was previously shown to neutralize the sporozoites of P. falciparum in the skin and blood before they could infect liver cells.
Malaria Treatments
Various antimalarial treatments are approved by the U.S. CDC in 2024.
Malaria Outbreaks
Malaria outbreak news is posted at Precision Vax. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), malaria is a mosquito-borne disease caused by a parasite. Unlike other diseases, exposure to malaria parasites does not confer lifelong protection and acquired immunity only partially protects people against future malaria diseases.
Malaria Vaccine News
April 25, 2024 - Benin, Liberia, and Sierra Leone launched malaria vaccinations targeting millions of children.
January 8, 2024 - Cameroon's Minister of Public Health confirmed the African country will introduce a malaria vaccine in January 2024.
October 12, 2023 - UNICEF, the world's largest single vaccine buyer, announced an agreement to secure a supply of the world's second malaria vaccine, R21/Matrix-M.
October 2, 2023 - The World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended a new vaccine, R21/Matrix-M, to prevent malaria in children.
August 22, 2023 - An editorial published in The Lancet says the WHO recommends that seasonal malaria vaccination with recombinant circumsporozoite protein-based RTS, S/AS01E, and chemoprevention, with sulfadoxine, pyrimethamine, and amodiaquine be administered monthly during the rainy season when malaria transmission peaks.
August 18, 2023 - GAVI reported that, as of mid-2023, 96.5% of eligible children in Vihiga, Kenya, have received at least one of four doses of the RTS,S vaccine.
July 11, 2023 - Based on discoveries by Scientific Co-founder Jonathan Kurtis, MD, Ph.D., Ocean Biomedical is working on a multivalent mRNA-based malaria vaccine with the potential to target several stages in the malaria cycle.
June 8, 2023 - Ocean Biomedical, Inc. announced a new patent for his malaria vaccine discoveries that may be used to prevent the parasite at multiple stages in the malaria cycle.
June 7, 2023 - The journal Vaccines published a new study: A mosquito AgTRIO mRNA vaccine contributes to immunity against malaria.
April 13, 2023 - The Republic of Ghana's FDA approved the R21/Matrix-M malaria vaccine.
January 25, 2023 - The Lancet published - Monoclonals against malaria: the promise of passive protection.