3 Additional Ebola Treatments Approved for Uganda

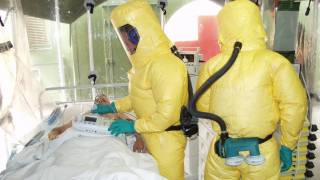
Uganda’s health minister said on Twitter that health workers have now been authorized to use 3 experimental Ebola treatments in the country.
Uganda health workers and people who came in contact with Ebola-infected people began receiving Merck’s V920 (rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP) investigational vaccine candidate on June 15, 2019.
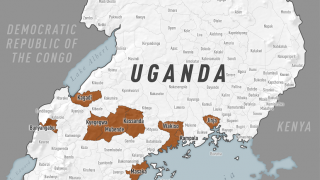
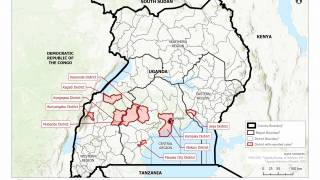
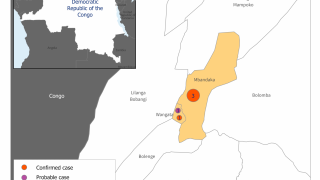
On Monday, June 17, 2019, Uganda reported it had vaccinated 128 people who have come into contact with the 3 confirmed Ebola cases.
“Happy to inform you all that we got clearance from both Uganda National Council for Science and Technology and National Drug Authority to bring in therapeutic treatment for Ebola patients in the country,” Uganda’s Health Minister, Jane Ruth Aceng, MBChB, MMed, MPH, is a Ugandan pediatrician, said June 18, 2019.
The treatments approved for shipment to Uganda:
- Mapp Biopharmaceutical’s ZMapp, which is composed of three “humanized” monoclonal antibodies manufactured in plants, specifically Nicotiana. It is an optimized cocktail combining the best components of MB‐003 (Mapp) and ZMAb (Defyrus/PHAC).
- Gilead Sciences’s Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc’s Regeneron and Remdesivir.
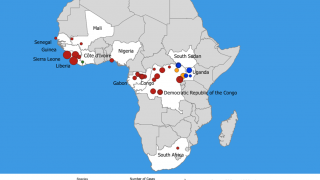
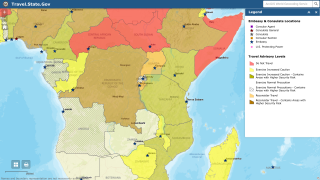
The U.N. health agency has said there have so far been no known cases of Ebola spreading between people in Uganda, all recorded patients had traveled in from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC).
Dr. Aceng said in another Tweet on June 18th ‘Uganda has not registered any new confirmed #Ebola case in Kasese District or any other part of #Uganda since the last registered case, which was 4 days ago.’
These experimental therapeutic treatments have already been used in the DRC.
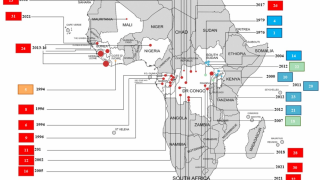
As of June 15, 2019, the current Ebola Zaire outbreak in the DRC has left over 2,168 people infected and 1,440 dead since August 2018.
The World Health Organization (WHO) Committee expressed its opinion on June 14, 2019, saying that ‘while the expanding Ebola Zaire outbreak in Africa is a health emergency, it does not meet all the criteria for a Public Health Emergency of International Concern declaration.’
In addition to the Ebola risk, Uganda notified the WHO on May 6, 2019, that they have declared a yellow fever outbreak.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee