Zika Vaccine Candidate Begins Human Testing

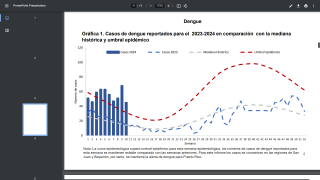
A new article published in The Lancet on February 10, 2019, reported positive findings from a first-in-human, phase 1a clinical trial of an investigational, purified, inactivated Zika virus vaccine (ZPIV) candidate.
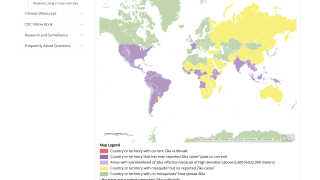
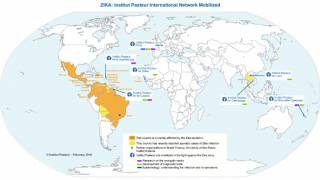
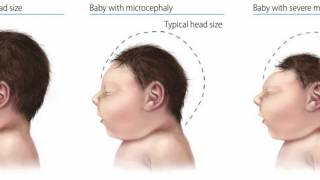
This is good news since the Zika virus has been found as a major cause of microcephaly and other neurologic defects ln infants says the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
ZPIV was found to be well-tolerated and elicited robust neutralizing antibody titers in healthy adults in 3 phase 1 studies.
The aggregate interim results from these 3 studies demonstrate that ZPIV has a tolerable safety profile and sufficient immunogenicity to provide potential clinical benefit.
The three trials are registered at ClinicalTrials.gov numbers: NCT02963909, NCT02952833, NCT02937233.
The three studies included in this aggregate analysis are all phase 1, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trials occurring at single sites, and are each designed to address a unique question about background immunity, vaccine dosage, or vaccination schedule.
The ZPIV vaccine candidate was developed, manufactured and provided to all sites by the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research (WRAIR).
ZPIV is a chromatographic column purified, formalin-inactivated Zika virus (PRVABC59), initially obtained from the CDC and cultivated and passaged in a qualified Vero cell line.
After purification and inactivation, ZPIV was diluted to 20 μg/mL and vialed in phosphate buffered saline (PBS), adsorbed 1:1 to aluminum hydroxide gel (Alhydrogel®, 2 mg/mL).
Each vial provided one 0.5 mL dose of 5 μg protein and 500 μg aluminum hydroxide adjuvant. Placebo formulations comprised PBS alone.
The WRAIR trial is assessing the impact of pre-existing flavivirus immunity conferred by priming with either a licensed yellow fever (YF-VAX®) or Japanese encephalitis (IXIARO®) vaccine followed by ZPIV vaccination.
The Saint Louis University (SLU) trial is evaluating safety and immunogenicity of three vaccine dosages (5 μg, 2.5 μg, 10 μg).
The Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) trial is evaluating three dosing schedules: two doses separated by either four or two weeks, or a single dose.
The current phase 1 trials are being modified to evaluate if a second boost (third dose) or higher dosage will yield more potent and sustained immunogenicity.
Recent Zika news:
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee