Tuberculosis Cases Reduced During 2017
There is good news to celebrate World Tuberculosis Day, 2018.
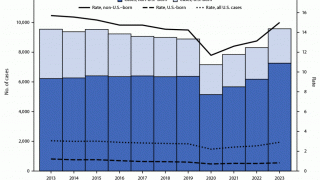
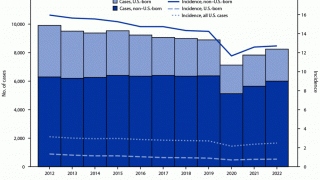
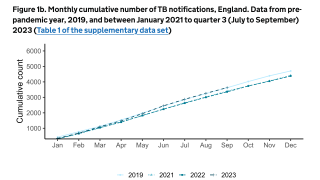
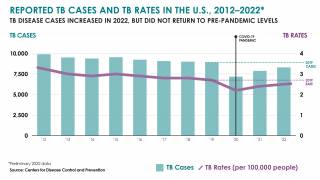
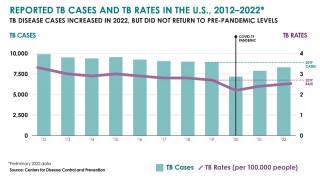
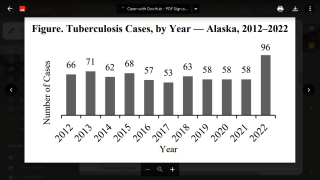
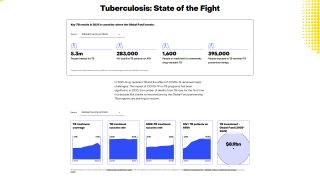
In 2017, a total of 9,093 new cases of tuberculosis (TB) were reported in the United States to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The case count decreased by 1.8 percent from 2016 to 2017, and the rate declined by 2.5 percent over the same time frame.
State-specific TB rates ranged from 0.3 in Montana to 8.1 in Hawaii, with a median state TB rate of 1.8 per 100,000 population.
Moreover, from a city perspective, New York City reported a 10 percent increase from 2016, with 613 TB cases in 2017.
Meanwhile there is still plenty of work ahead to eliminate this costly, lung disease.
Multidrug-resistant (MDR) tuberculosis treatment comes at a high price, ranging from $50,000 to over $500,000.
To achieve TB elimination by the year 2100, the annual decline in cases needs to increase to 3.9 percent.
“Eliminating TB in the United States will require a sustained effort to control TB disease, and expanding testing and treatment of latent TB infection to prevent the development of TB disease, said Philip LoBue, MD, FACP, FCCP, Director, Division of Tuberculosis Elimination, National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention.
World TB Day commemorates the date in 1882 when Dr. Robert Koch announced his discovery of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacillus that causes tuberculosis.
This bacteria usually spread through the air and attacks the lungs, but TB bacteria can attack any part of the body such as the kidney, spine, and brain, says the CDC.
People with tuberculosis may experience symptoms similar to the flu, or no symptoms at all. In the later stages, people with tuberculosis can develop a cough with mucus that becomes progressively thick, bloody or yellow, chest pain, shortness of breath and possibly red or cloudy urine.
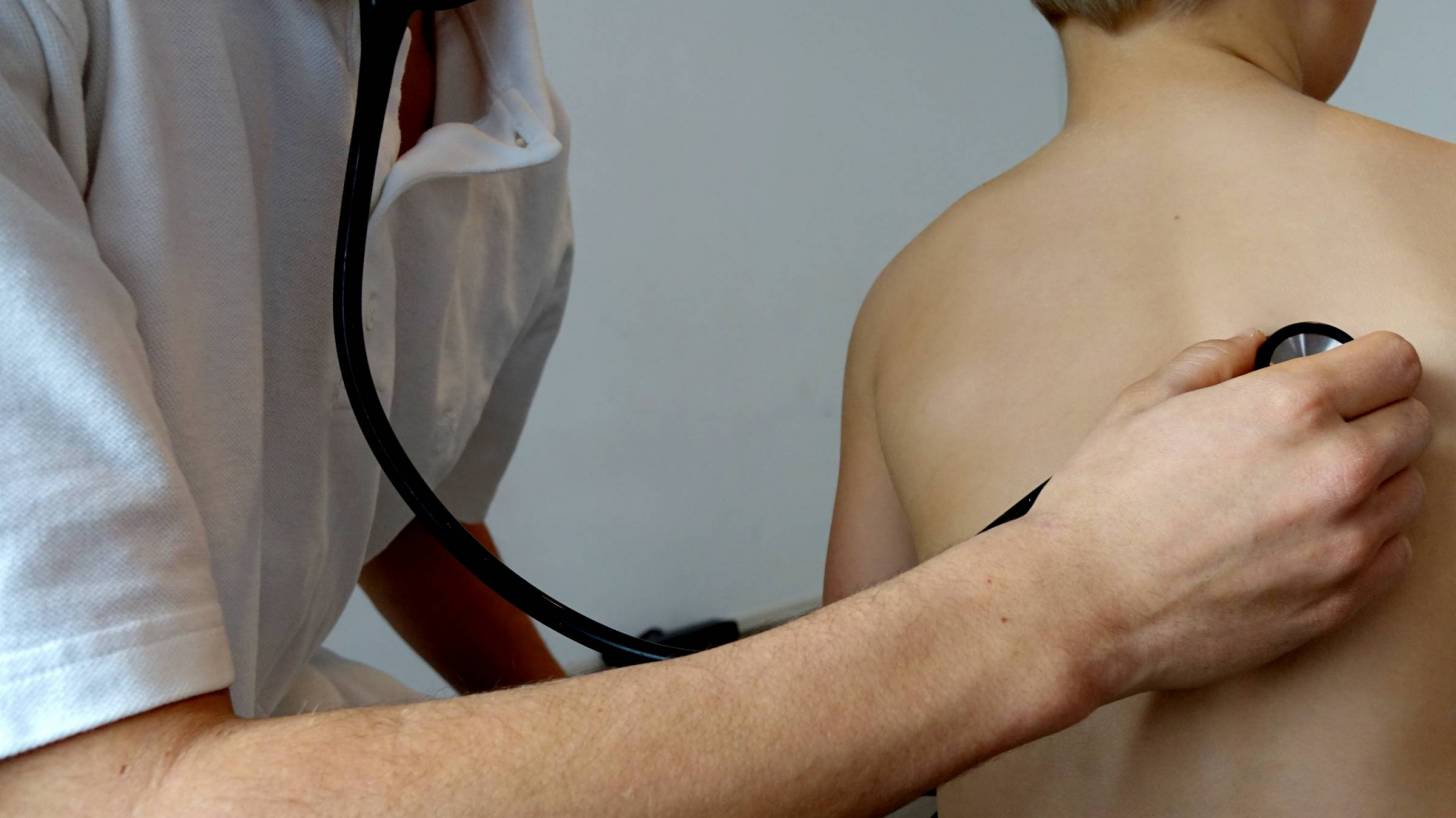
Tuberculosis testing, also known as the PPD test, is a skin test used to determine if someone has developed an immune response to the bacterium that causes tuberculosis, says the CDC.
The PPD test generally costs less than $100 in the USA. There are also blood tests for TB.
The best TB prevention in countries where TB is very common is often a vaccine.
Named after the French scientists who developed it, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) was first used in 1921 and had been classified to work for only 10 to 15 years.
But new research found that the BCG vaccine protects half of those who received the vaccination by the age of 12, were still protected for at least 20 years.
Lead author of this study Dr. Punam Mangtani, Associate Professor in Epidemiology at the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine, said, “BCG is not perfect but until a new, more effective vaccine is approved and rolled-out, we should be maximizing its potential."
An alternative TB vaccine may be on its way to market.
An early-stage vaccine candidate, MTBVAC, has been the only live attenuated M. tuberculosis vaccine approved to enter into clinical trials.
The promising results of the Phase I study led to a Dose-escalation Safety and Immunogenicity Study to Compare MTBVAC to BCG in Newborns With a Safety Arm in Adults (MTBVAC-Ph1b),
Recently, a study by Aguilo et al, at the University of Zaragoza provided the first evidence that two M. tuberculosis antigens of MTBVAC, ESAT-6, and CFP-10, which are both not present in BCG, are key contributors to the superior protection that is induced by MTBVAC, in mice.
An MTBVAC phase 2a study in South Africa is planned to begin in 2018.
Several pharmacies in the USA offer the BCG vaccine.
The CDC Vaccine Price List provides the private sector prices for the BCG vaccine
Vaccines, like any medicine, can have side effects, says the CDC. You are encouraged to report negative side effects of vaccines to the FDA or CDC.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee