Global Influenza Strategy for 2019-2030 Announced

The World Health Organization (WHO) released a Global Influenza Strategy for 2019-2030, which is aimed at protecting people in all countries from the threat of influenza.
The goals of this new strategy are to prevent seasonal influenza, control the spread of influenza from animals to humans, and prepare for the next influenza pandemic.
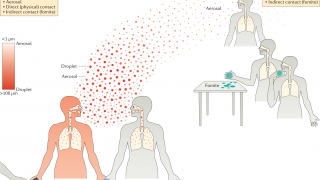
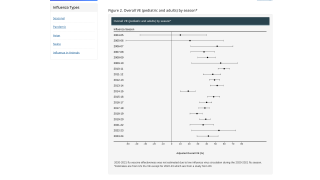
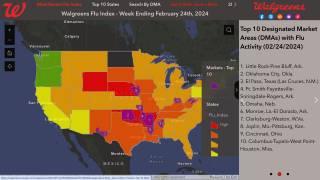
Influenza remains one of the world’s greatest public health challenges. Influenza virus is a respiratory pathogen that causes annual influenza epidemics affecting an estimated 15 percent of the global population, with up to 645,000 deaths annually.
In addition, pandemic variants of the Influenza A virus have previously been associated with upwards of 50 million deaths worldwide, says the WHO.
“The threat of pandemic influenza is ever-present,” said WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus in a press release. “The ongoing risk of a new influenza virus transmitting from animals to humans and potentially causing a pandemic is real.”
“The question is not if we will have another pandemic, but when.”
We must be vigilant and prepared – the cost of a major influenza outbreak will far outweigh the price of prevention.”
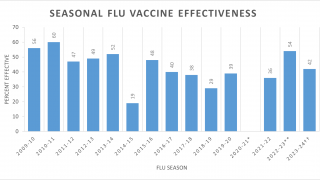
The WHO recommends an annual influenza vaccination as the most effective way to prevent influenza. Vaccination is especially important for people at higher risk of serious influenza complications and for healthcare workers.
This new strategy is the most comprehensive and far-reaching that WHO has ever developed for influenza. It outlines a path to protect populations every year and helps prepare for a pandemic through strengthening routine programmes.
The Global Influenza Strategy for 2019-2030 has 2 overarching goals:
- Build stronger country capacities for disease surveillance and response, prevention and control, and preparedness. To achieve this, it calls for every country to have a tailored influenza programme that contributes to national and global preparedness and health security.
- Develop better tools to prevent, detect, control and treat influenza, such as more effective vaccines, antivirals, and treatments, with the goal of making these accessible for all countries.
“With the partnerships and country-specific work we have been doing over the years, the world is better prepared than ever before for the next big outbreak, but we are still not prepared enough,” said Dr. Tedros.
“This strategy aims to get us to that point. Fundamentally, it is about preparing health systems to manage shocks, and this only happens when health systems are strong and healthy themselves.”
To successfully implement this strategy, effective partnerships are essential. WHO will expand partnerships to increase research, innovation, and availability of new and improved global influenza tools to benefit all countries.
At the same time WHO will work closely with countries to improve their capacities to prevent and control influenza.
The new influenza strategy builds on and benefits from successful WHO programs. For more than 65 years, the Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System (GISRS), comprised of WHO Collaborating Centres and national influenza centers, have worked together to monitor seasonal trends and potentially pandemic viruses. This system serves as the backbone of the global alert system for influenza.
Important to the strategy is the ongoing success of the Pandemic Influenza Preparedness Framework, a unique access and benefit sharing system that supports the sharing of potentially pandemic viruses, provides access to life-saving vaccines and treatments in the event of a pandemic and supports the building of pandemic preparedness capacities in countries through partnership contributions from industry.
The strategy meets one of WHO’s mandates to improve core capacities for public health, and increase global preparedness and was developed through a consultative process with input from Member States, academia, civil society, industry, and internal and external experts.
Supporting countries to strengthen their influenza capacity will have collateral benefits in detecting infection in general, since countries will be able to better identify other infectious diseases like Ebola or Middle East respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus (MERS-CoV).
Through the implementation of the new WHO global influenza strategy, the world will be closer to reducing the impact of influenza every year and be more prepared for an influenza pandemic and other public health emergencies.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee