CDC Flu News: Week #4

The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has issued its weekly influenza report, as of February 1, 2019.
This CDC report indicates a reduced expansion rate in flu illnesses, medical visits, and hospitalizations when compared to Week #3 data.
As of January 26, 2019, the CDC’s Week #4 report is estimating the impact of the 2018/19 flu season as follows:
- 10,100,000 – 11,700,000 symptomatic illnesses,
- 4,700,000 – 5,600,000 medical visits; and,
- 118,000 – 141,000 hospitalizations.
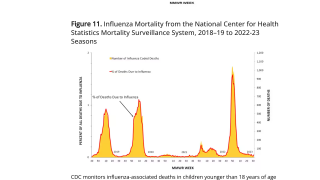
Unfortunately, 2 additional influenza-associated pediatric deaths were reported during Week #4, which increases the 2018-2019 flu season total to 24.
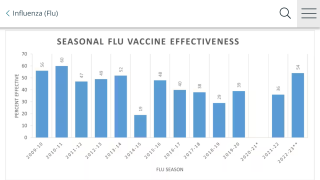
Separately, 2 recent reports indicate this season’s influenza vaccines are being effective.
In Canada, the influenza vaccine has been reported to be 72% effective this season against the influenza A(H1N1), offering “substantial” protection, researchers said on January 24, 2019.
An early-season estimate of flu vaccine effectiveness (VE) against hospitalization for influenza in children in Hong Kong has found 90% VE, according to a report in Eurosurveillance on January 29, 2019.
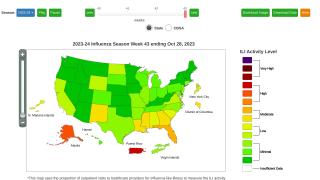
The details for Week #4, ending January 26, 2019, are as follows:
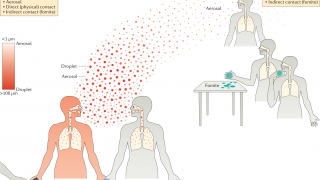
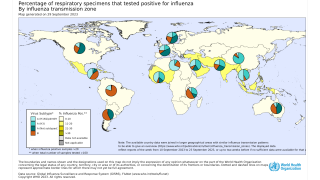
- The percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza viruses in clinical laboratories increased. Influenza A viruses have predominated in the United States since the beginning of October. Influenza A(H1N1) viruses have predominated in most areas of the country, however, influenza A(H3) viruses have predominated in the southeastern United States (HHS Region 4).
- The majority of influenza viruses characterized antigenically and genetically are similar to the cell-grown reference viruses representing the 2018–2019 Northern Hemisphere influenza vaccine viruses.
- The vast majority of influenza viruses tested (>99%) show susceptibility to oseltamivir and peramivir. All influenza viruses tested showed susceptibility to zanamivir.
- The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) increased to 3.8%, which is above the national baseline of 2.2%. All 10 regions reported ILI at or above their region-specific baseline level.
- New York City and 23 states experienced high ILI activity; Puerto Rico and 10 states experienced moderate ILI activity; the District of Columbia and 13 states experienced low ILI activity.
- Puerto Rico and three states reported regional activity; two states reported local activity; the District of Columbia and the U.S. Virgin Islands reported sporadic activity, and Guam did not report.
- A cumulative rate of 15.3 laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations per 100,000 population was reported. The highest hospitalization rate is among adults 65 years and older (39.8 hospitalizations per 100,000 population).
- The proportion of deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza (P&I) was at the system-specific epidemic threshold in the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) Mortality Surveillance System.
In the USA, antiviral medications and various flu vaccines are available in most pharmacies.
The CDC Vaccine Price List provides the private sector vaccine prices for general information.
And, flu vaccine discounts can be found here.
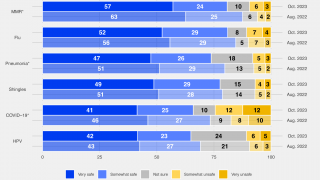
Vaccines, like any medicine, can have side effects. Vaccine patients are encouraged to report negative side effects of vaccines to the CDC.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee