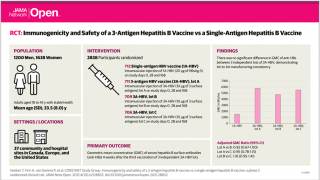
Foreign-Born Women of Reproductive Age Lack Hep B Vaccinations
A new research study reported foreign-born women have a greater lifetime exposure to hepatitis B virus, than US-born women.
This study found the hepatitis B vaccination coverage among reproductive-aged women was 33 percent lower for foreign-born women (27.3%), when compared to US-born women (40.9%).
This is not good news, since about 80 percent of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infected women who gave birth in the United States during 2006, were born in other countries.
When segmented on a country basis, HBV vaccination coverage was reported to be low for women born in the Caribbean islands (18.4%), South America (25.3%), and the Indian subcontinent (31.7%).
Additionally, HBV vaccination was also low among women who had been in the United States less than 15 years (23.7%) and those who were not US citizens (23.8%).
Worldwide estimates suggest that more than 2 billion people have been infected with HBV, and that 248 million of these people are chronically infected.
About 15% to 25% of persons with chronic HBV infection die from cirrhosis or liver cancer.
These researchers said, “Until HBV screening and vaccination rates among women of childbearing ages are addressed, Mother-to-Child Transmission (MTCT) of hepatitis B will likely continue to occur in the United States.”
MTCT of hepatitis B leads to acute infection in up to 90% of infants born to infected mothers, reports the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
In the United States, women of reproductive age who seek medical care are not universally offered the hepatitis B vaccine.
The American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) considers hepatitis B vaccination during pregnancy to be safe and recommends specifically that susceptible pregnant women who are at risk for HBV infection should be vaccinated.
Three doses of the vaccine are recommended for full immunity, and 25% of US adults aged 19 years and older had received three or more doses in 2015.
Separately, during April 2018, the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), reported one hepatitis B vaccine delivers the best prevention from this type of hepatitis.
The ACIP is now recommending Heplisav-B (HepB-CpG) for adults over the age of 18 years old.
Heplisav-B was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) during November 2017 and is the 5th inactivated Hepatitis B vaccine currently recommended by the FDA.
Heplisav-B is a yeast-derived vaccine prepared with a novel adjuvant, administered as a 2-dose series, over 1 month. HepB-CpG is available in single-dose 0.5 mL vials.
The CDC Vaccine Price List provides current HBV vaccine contract prices and general information, and vaccine discounts can be found here.
Vaccines, like any medicine, can have side effects, says the CDC. You are encouraged to report negative side effects of vaccines to the FDA or CDC.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee