GSK Licenses TB Vaccine Candidate to Gates Institute

London based GSK announced that it has licensed its M72/AS01E tuberculosis disease (TB) vaccine candidate to the Bill & Melinda Gates Medical Research Institute (MRI).
This transaction announced on January 27, 2020, paves the way for the continued development of the vaccine M72/AS01E candidate.
The Gates MRI will take the lead on future vaccine candidate development and GSK will provide the AS01 adjuvant for this development program.
This is good news since there is no approved vaccine capable of preventing pulmonary TB disease in adolescents and adults, who accounted for 89 percent of people who fell ill with TB in 2018.
Furthermore, there is no effective way to prevent the spread of TB, which is a contagious bacterial disease, and tools for diagnosing and treating the disease are also inadequate.
Dr. Thomas Breuer, Chief Medical Officer of GSK Vaccines, commented in a press release “At GSK, we are very proud to have developed a TB vaccine candidate which has shown promising clinical trial results in adolescents and adults where the need to combat the TB epidemic is greatest.”
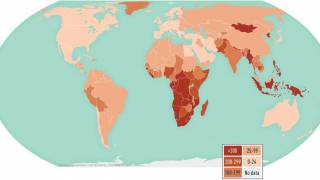
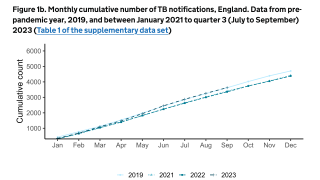
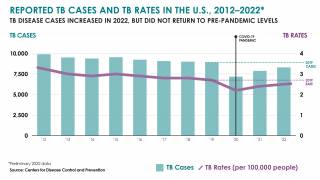
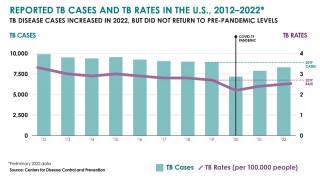
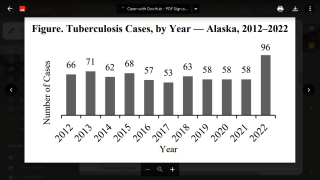
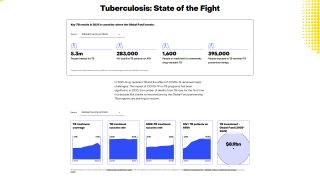
TB is the world’s deadliest infectious disease, with 10 million new cases and 1.5 million deaths in 2018 alone. The TB disease burden is concentrated in low- and middle-income countries.
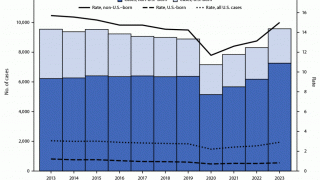
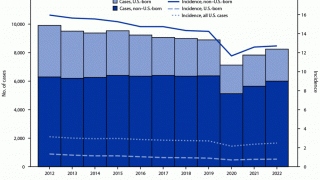
In 2018, a total of 70.2 percent of reported TB cases in the USA occurred among non-U.S.-born people. Among U.S. states, the majority of TB cases were reported from 4 states: California (23.2%), Texas (12.5%), New York (8.3%), and Florida (6.5%), reports the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
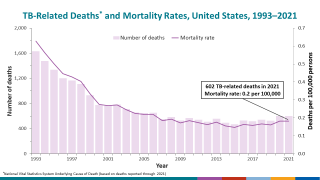
In 2017, 515 deaths in the USA were attributed to TB. This is a decrease from 528 deaths attributed to TB in 2016, says the CDC.
The M72/AS01E vaccine candidate contains the M72 recombinant fusion protein, derived from two Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens (Mtb32A and Mtb39A), combined with the Adjuvant System AS01.
The vaccine candidate has been developed by GSK in conjunction with IAVI.
The live attenuated vaccine, Bacille Calmette-Guerin (BCG), has been in use for nearly a century, and while it is effective in preventing severe TB disease in infants and young children, it provides limited protection against pulmonary TB in adolescents and adults.
Recently, a new study found that simply changing the delivery method of tuberculosis vaccination could dramatically boost its effectiveness.
Announced on January 1, 2020, in collaboration with the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Pitt Med researchers discovered that intravenous TB vaccination with BCG was highly protective against the infection in monkeys, compared to the standard injection directly into the skin, which offers minimal protection.
TB is also the leading killer of people living with HIV, accounting for one-third of deaths among HIV-positive people. The world’s most vulnerable populations are disproportionately affected by TB, with many cases of TB occurring in resource-limited areas.
Funding for research that uncovered the potential of M72 was provided by the United Kingdom’s Department for International Development, the Directorate-General for International Cooperation in the Netherlands, the Australian Department for Foreign Affairs and Trade, the European Commission and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
GSK is a science-led global healthcare company with a special purpose: to help people do more, feel better, live longer.
The Bill & Melinda Gates Medical Research Institute is a non-profit biotech organization. Our mission is to develop products to fight malaria, tuberculosis, diarrheal diseases and improve outcomes in maternal and newborn health — major causes of mortality, poverty, and inequality in Low- and Middle-Income Countries.
Tuberculosis vaccine news published by Precision Vaccinations.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee