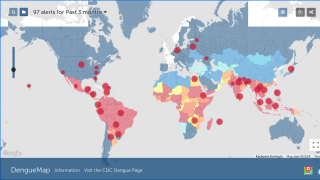
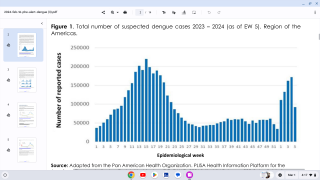
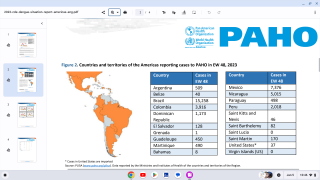
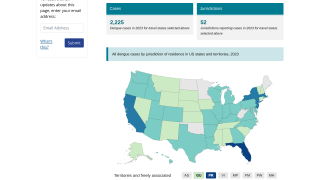
NIH and University of Maryland Conducting Universal Mosquito-Borne Diseases Vaccine Study

A London-based clinical development services business confirmed the launch of Phase 1 clinical trial for AGS-v PLUS, an experimental vaccine designed to protect against many different mosquito-borne diseases, including the Zika virus.
hVIVO plc announced in a July 31, 2019, press release that the vaccine candidate, AGS-v PLUS, was developed by Imutex Limited.
The AGS-v PLUS vaccine is a mosquito-borne disease vaccine with a novel proposed dual action mechanism of preventing infection in humans while controlling the mosquito population.
AGS-v is composed of 4 salivary peptides isolated from Anopheles gambiae salivary glands, but that are common across a number of mosquitoes.
This limited clinical trial will test the AGS-v PLUS vaccine’s safety and immunogenicity when given with or without adjuvant to small groups of healthy volunteers.
This 50 participant phase 1 study updated on July 16, 2019, says it will be randomly assigned five groups for approximately 12 months. During this time, they will attend several study visits, which may include physical examinations, blood collection, skin biopsies, and a mosquito feeding procedure.
Trevor Phillips, Executive Chairman of hVIVO, said in this press release, "It is great to see the relationship with NIH and the University of Maryland School of Medicine continues as AGS-v PLUS, one of the assets in our joint venture Imutex, moves into the clinic.”
The remaining study endpoints will be evaluated once the full and final data are available, at which point a full assessment of the trial results will be possible when the NIH completes the sample analyses.
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the NIH, previously tested an earlier version of this vaccine, AGS-v, in a first-in-human trial conducted in NIAID’s Laboratory of Infectious Diseases’ Special Clinical Studies Unit at the NIH Clinical Center in Bethesda, Maryland, and final results of this trial are expected in due course.
This National Institutes of Health (NIH) supported study is located at the University of Maryland School of Medicine.
Additionally, this study received funding from the UK Department of Health and Social Care, managed by Innovate UK.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee
- A Phase 1 clinical trial of AGS-v PLUS a Universal mosquito-borne diseases vaccine candidat
- Evaluating the Safety and Immunogenicity of AGS-v PLUS, a Universal Mosquito-Borne Disease and Mosquito Control Vaccine
- Study in Healthy Volunteers to Evaluate the Safety and Immunogenicity of AGS-v, a Universal Mosquito-Borne Disease Vaccine
- AGS-v – a universal mosquito-borne diseases vaccine candidate