Ebola Test OraQuick Approved by the FDA
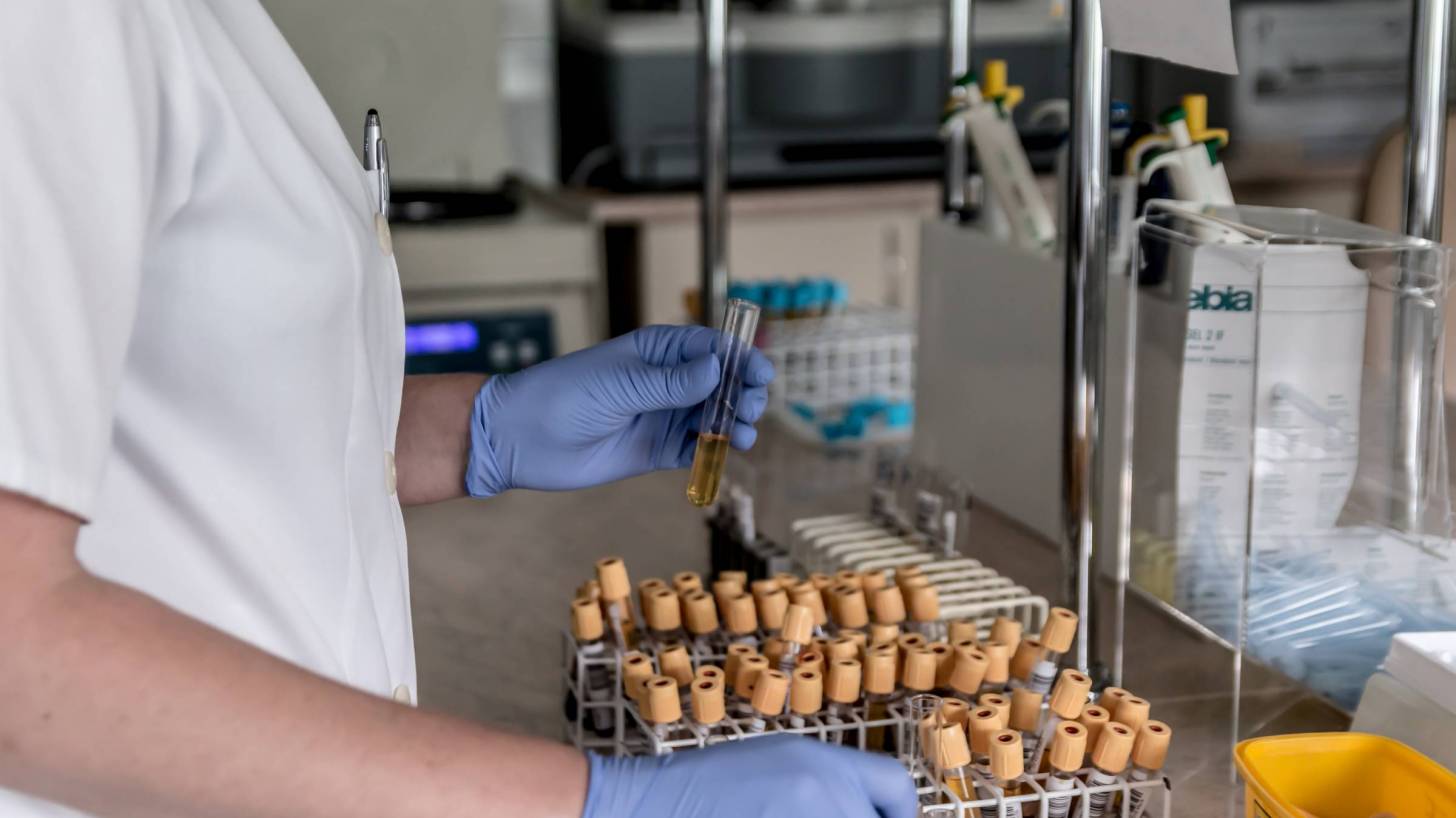

The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced the marketing approval of a rapid diagnostic test (RDT) to detect Ebola virus antigens in human blood from certain living individuals.
The OraQuick Ebola Rapid Antigen test provides a rapid, presumptive Ebola diagnosis, that must be confirmed.
Furthermore, a negative test result does not rule out Ebola virus infection.
This new test is the first RDT the FDA has allowed to be marketed in the U.S. for the Ebola Virus Disease (EVD).
Acting FDA Commissioner Ned Sharpless, M.D., said in a press release published on October 10, 2019, “Investigational Ebola Zaire vaccines and therapeutics have shown promising results, but one of the most important tools in stopping these outbreaks is quickly diagnosing patients and supporting safe and dignified burials.”
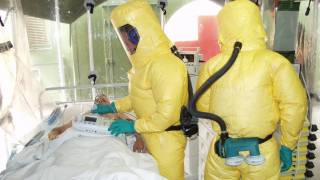
“This device could be used to reduce the risk of transmission during those burials.”
Innovative Ebola Zaire preventive vaccines currently administered in central Africa include Merck’s V920 (rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP) a recombinant, replication-competent Ebola vaccine and Jannsen’s Ad26.ZEBOV/MVA-BN a heterologous prime-boost Ebola vaccine regimen.
And, Ebola therapeutic medications REGN-EB3 and mAb114 continue to be evaluated.
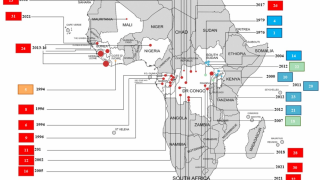
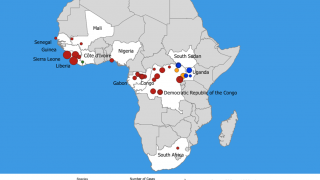
Previously, during the 2014 Ebola outbreak, the Secretary of the Department of Health and Human Services declared that circumstances justified the authorization of emergency use of in vitro diagnostics for the detection of the Ebola virus.
At the time, the FDA worked with CDC and test developers to make diagnostic tests, including the OraQuick Ebola Test, available through the Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) pathway.
Since 2014, the FDA has authorized a number of diagnostic tests for Ebola under the EUA pathway to assist with the public health response.
For the OraQuick Ebola Test submission, the FDA reviewed data from multiple clinical studies of blood samples and cadaveric oral fluid from the 2014 West African outbreak and from a variety of analytical studies.
Based on these data, the FDA determined that general and special controls were necessary to provide reasonable assurance of the safety and effectiveness of the OraQuick Ebola Test when intended to identify antigens associated with the Ebola virus in blood from symptomatic patients and oral fluid of cadavers.
The studies demonstrated the importance of testing only symptomatic individuals so that the amount of virus is high enough to be detectable by this test.
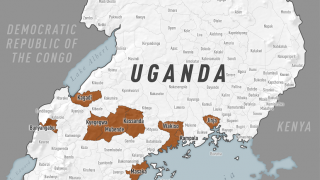
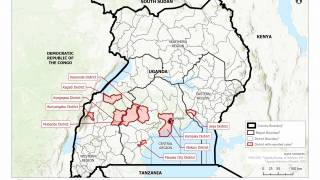
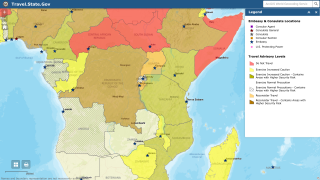
Therefore, the OraQuick Ebola Test is intended for use in patients suspected of and with signs or symptoms consistent with EVD, and when the patient meets the CDC’s Ebola virus epidemiological criteria, such as a history of residence in or travel to a geographic region with active EVD transmission at the time of travel.
The OraQuick Ebola Test is not intended to be used for general Ebola infection screening (e.g., airport screening) or testing of individuals at risk of exposure without observable signs of infection.
The definitive identification of EVD requires additional testing and confirmation procedures (such as by a more sensitive but less rapid polymerase chain reaction test) and in consultation with public health and/or other authorities to whom reporting is required.
The OraQuick Ebola Test was reviewed under the De Novo premarket review pathway, a regulatory pathway for low-to-moderate-risk devices of a new type. Along with this marketing authorization, the FDA is establishing criteria, called special controls, that determine the requirements for demonstrating accuracy, reliability and effectiveness of tests intended to identify Ebola virus antigens.
Recent Ebola Zaire disease news
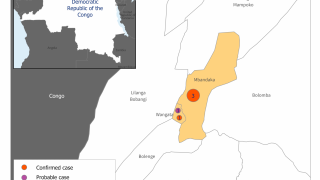
- Unknown Ebola Risk Discussed in Tanzania
- Ebola Treatment Receives $14 Million Dollar Advanced Development Support
The FDA, an agency within the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, promotes and protects the public health by, among other things, assuring the safety, effectiveness, and security of human and veterinary drugs, vaccines and other biological products for human use, and medical devices.
Ebola news is published by Precision Vaccinations
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee