GSK today announced positive results from the pivotal phase III trial for gepotidacin, a potential first-in-class oral antibiotic with a novel mechanism of action for uncomplicated urogenital gonorrhea in adolescents and adults.
The study's results showed that gepotidacin (oral, two doses of 3,000mg) was non-inferior, with 92.6% success rates, compared to 91.2% success rates for intramuscular (IM) ceftriaxone (500mg) plus oral azithromycin (1,000mg) combined therapy, a leading combination gonorrhea treatment regimen.
Chris Corsico, SVP of Development, GSK, said in a press release on April 17, 2024, "We are committed to working with health regulators globally to introduce this potential new antibiotic, focusing on solutions that meet critical patient needs."
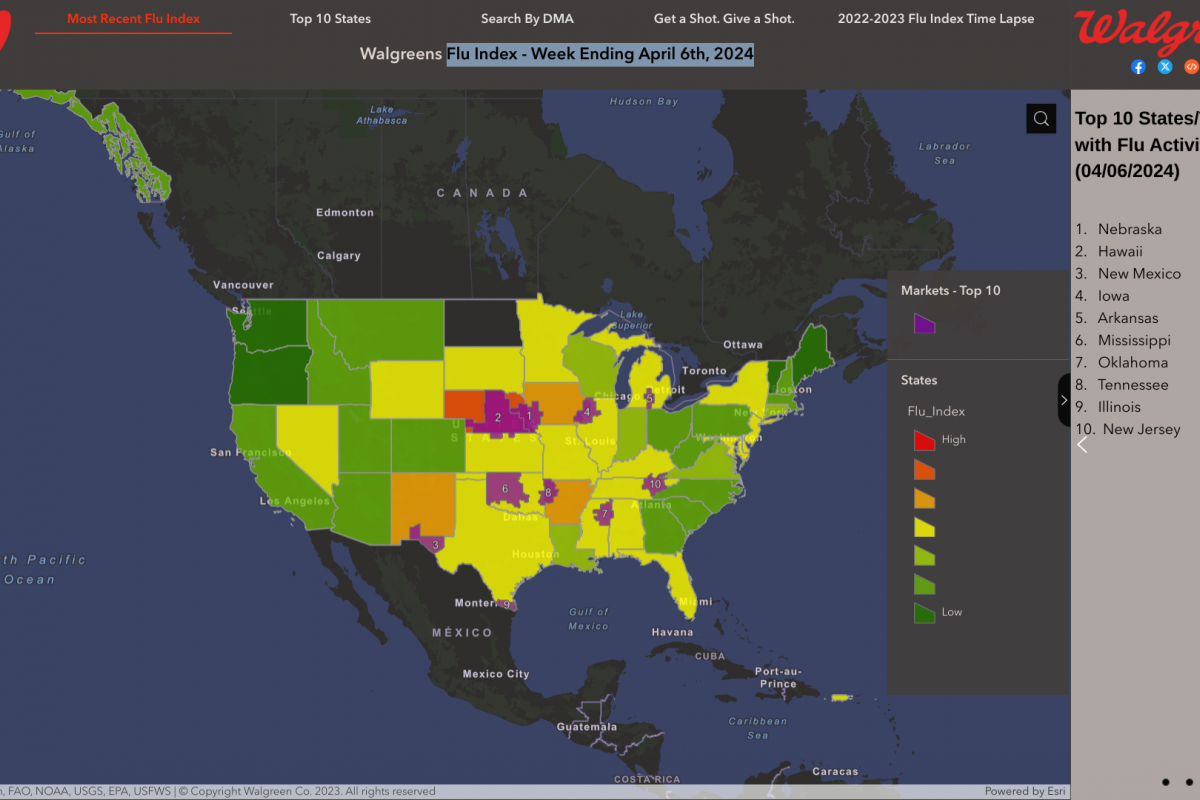
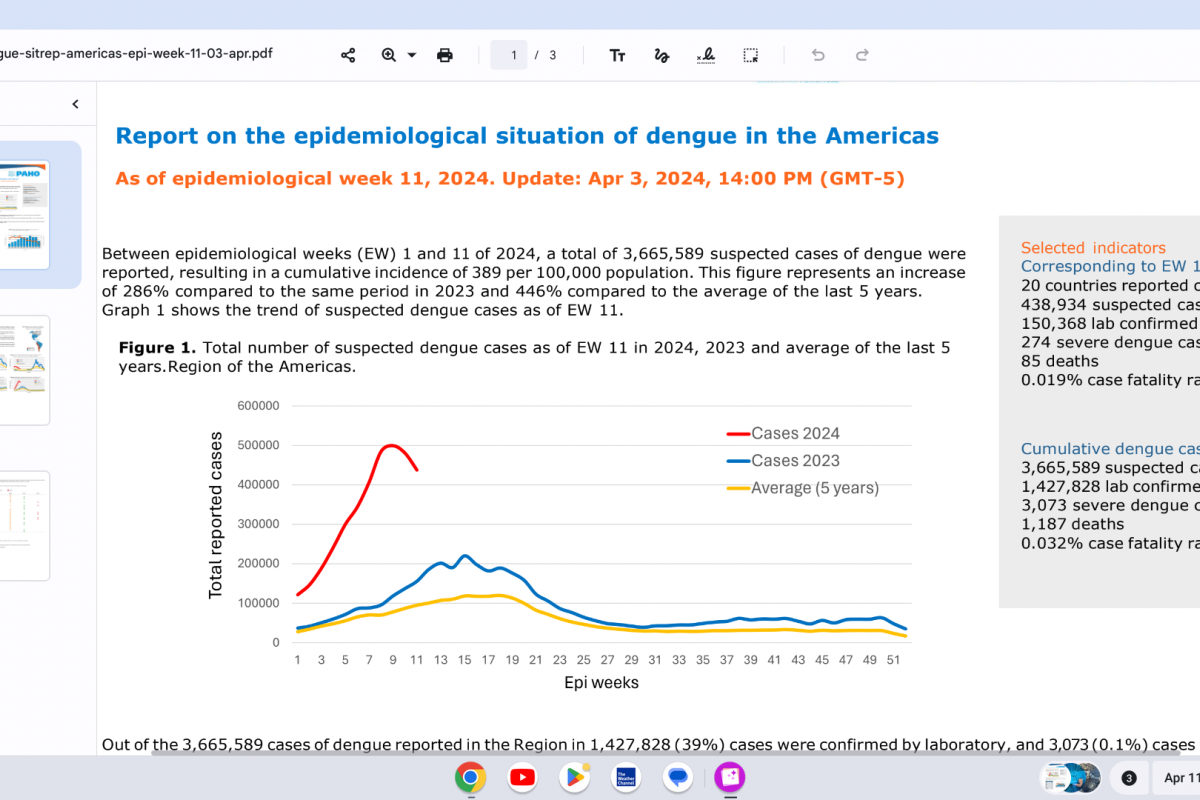
This announcement is important since the U.S. CDC previously reported that approximately half of the gonorrhea cases each year in the US are resistant to one antibiotic.
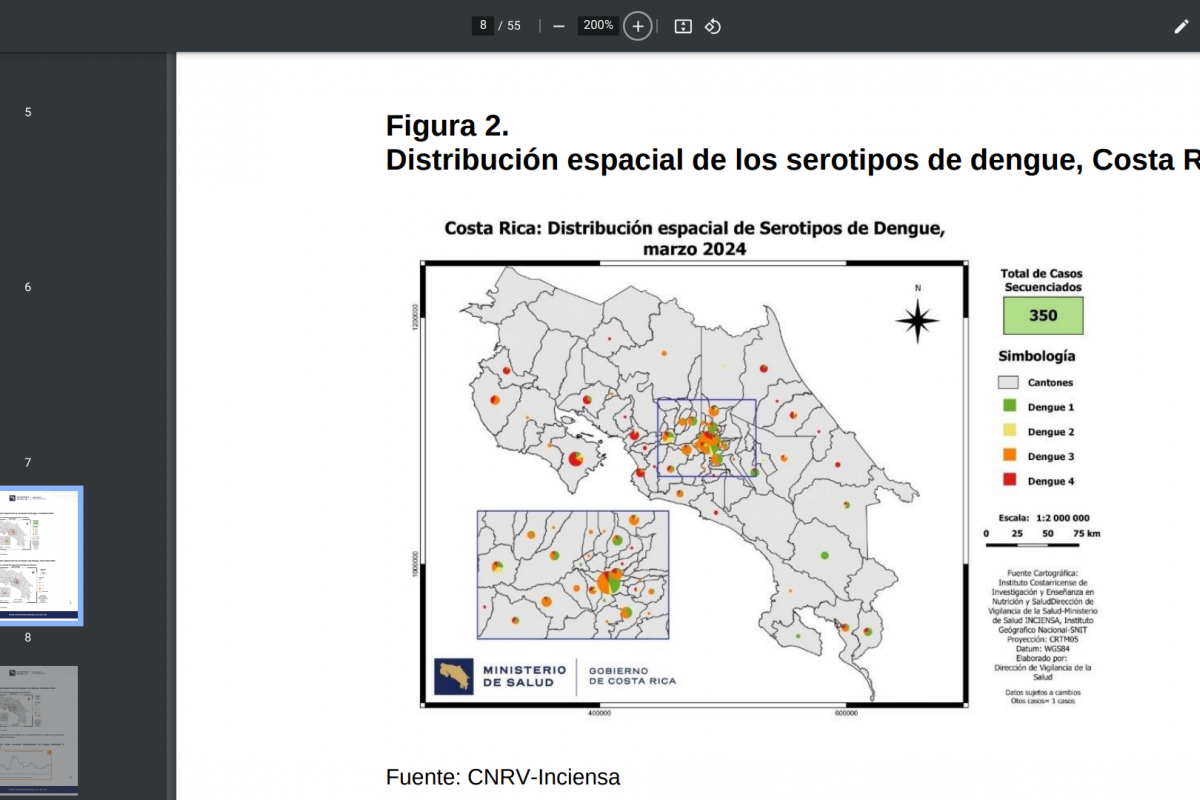
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection caused by bacteria called Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which the World Health Organisation has recognized as a priority pathogen. If inadequately treated, it can lead to infertility and other sexual and reproductive health complications.
Additionally, GSK is developing gepotidacin to potentially treat uncomplicated urinary tract infections (uUTs). If approved, Gepotidacin could be the first uUTI oral antibiotic in over twenty years.
The development of gepotidacin has been funded in whole or in part with U.S. federal funds.
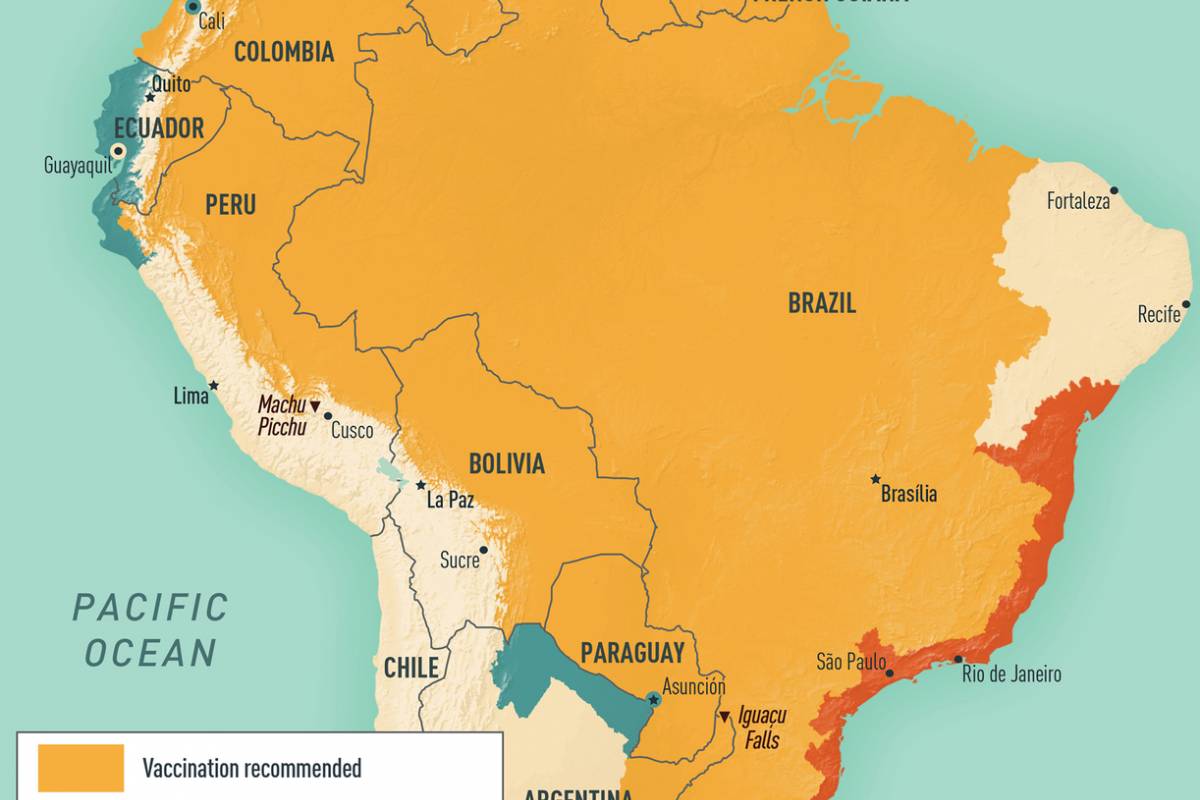
From a prevention perspective, there are no approved gonorrhea vaccines., but a repurposed meningococcal vaccine has been reported effective.
And the is an oral spray UTI vaccine (Uromune™, MV140) being evaluated in 26 countries in 2024.