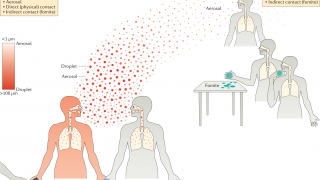
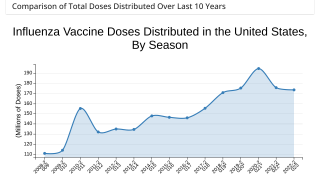
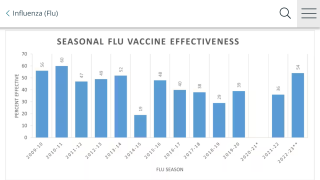
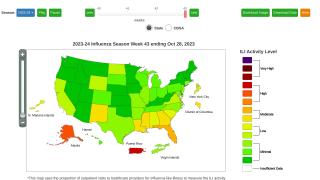
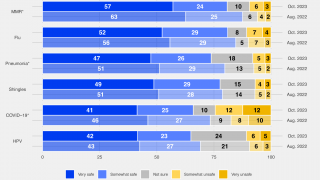
Northern Hemisphere Flu Season Is Ending

There is some good ‘flu news’ reported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) during Week #17 of the 2018-2019 influenza season.
The CDC reported the influenza activity across the USA was below the national baseline, for the 2nd week in a row.
The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) decreased to 1.8 percent, which is below the national baseline of 2.2 percent.
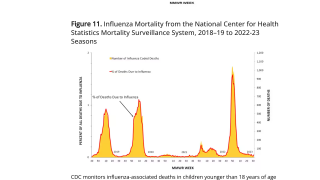
The CDC did publish more bad news regarding pediatric deaths during this flu season. During Week #17, there were 5 additional fatalities reported as of April 27, 2019.
Three of these deaths were associated with an influenza A(H3) virus.
This new CDC data increases the total number of pediatric deaths to 101 during the 2018-2019 flu season.
Further estimates project a total number of adult deaths related to various influenza viruses to reach between 36,100 to 59,600 adults.
Additional CDC flu season estimates include:
- 37,200,000 – 42,700,000 symptomatic illnesses
- 17,200,000 – 20,000,000 medical visits
- 524,000 – 637,000 hospitalizations
While influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses predominated from October 2018 to mid-February 2019, influenza A(H3N2) viruses have been more commonly identified since late February.
Below is a summary of the key influenza indicators for Week #17 ending April 27, 2019:
- The percentage of respiratory specimens testing positive for influenza viruses in clinical laboratories decreased. During the most recent three weeks, influenza A(H3) viruses were reported more frequently than influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses nationally, and in all 10 HHS Regions.
- The vast majority of influenza viruses tested (>99%) show susceptibility to oseltamivir and peramivir. All influenza viruses tested showed susceptibility to zanamivir.
- Puerto Rico experienced high ILI activity; four states experienced low ILI activity; New York City, the District of Columbia and 46 states experienced minimal ILI activity; and the U.S. Virgin Islands had insufficient data.
- A cumulative rate of 64.7 laboratory-confirmed influenza-associated hospitalizations per 100,000 population was reported. The highest hospitalization rate is among adults 65 years and older (216.6 hospitalizations per 100,000 population).
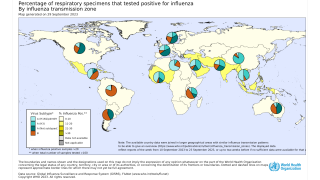
Additionally, the World Health Organization (WHO) reported on April 29, 2019, seasonal influenza A viruses accounted for the majority of detections in the Northern Hemisphere this year.
Moreover, if you are planning to visit a country in the ‘Southern Hemisphere’, influenza detections increased in southern Australia and South Africa. And, the influenza activity in South America remained at inter-seasonal levels, says the WHO.
This means you may need to get the flu shot recommended for those countries 10-days prior to departure.
Since there are various flu vaccines available and the vast majority of influenza viruses show susceptibility to antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir, peramivir, and zanamivir, it is best to discuss your personal needs with a healthcare provider.
Influenza vaccine discounts and financial assistance can be found at Vaccine Discounts.
Relevant Links: CDC vaccination schedules, CDC vaccine price list, international travel alerts, and report vaccine side effects.
Our Trust Standards: Medical Advisory Committee